Guide To The Conditions That Cause Hypopigmentation
Psoriasis
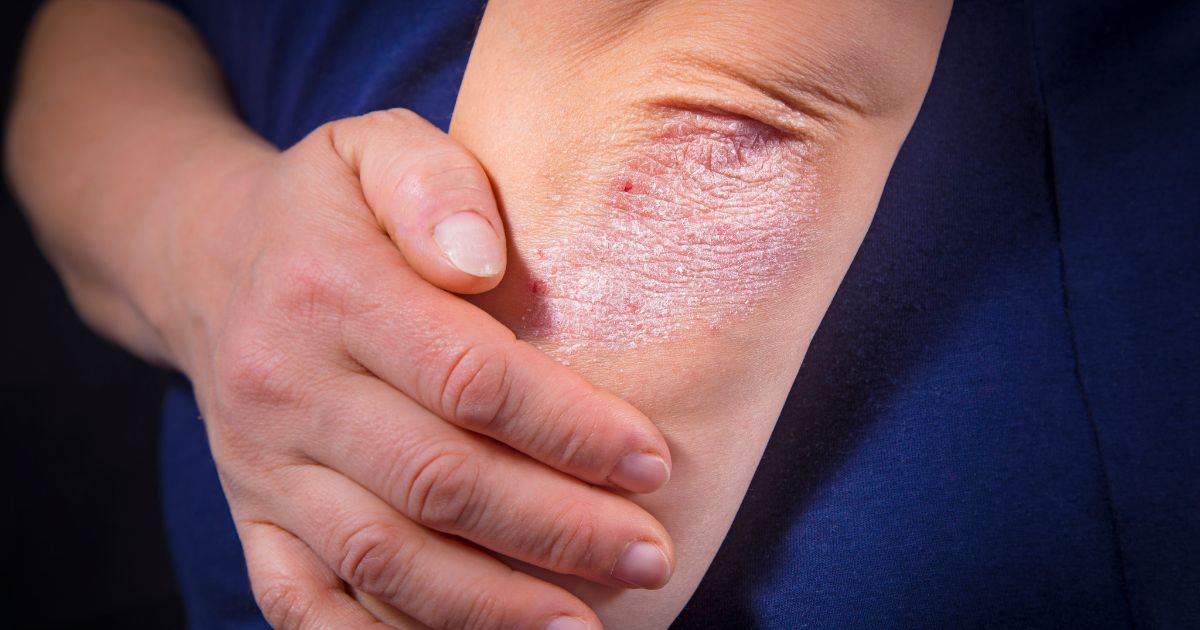
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that can include periods of remission and flare-ups. The condition speeds up the typical life cycle of the skin, resulting in a rapid accumulation of extra skin cells on the skin's surface. These patches are generally scaly and dry, and they may sometimes bleed or become painful. These patches can be red, though they may also appear pale and silvery if they turn into hypopigmented patches. Patients might also experience joint pain or swelling. To manage psoriasis, patients may need to use topical corticosteroids or retinoids, and light therapy might be considered. Patients who have severe forms of psoriasis that have not responded to conservative treatments may be prescribed oral or injectable medication. Methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics such as apremilast or secukinumab could be recommended. Thioguanine or hydroxyurea may also be beneficial.
Uncover more details on conditions that may cause hypopigmentation now.