Causes And Risk Factors Of De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
Inflammatory Conditions
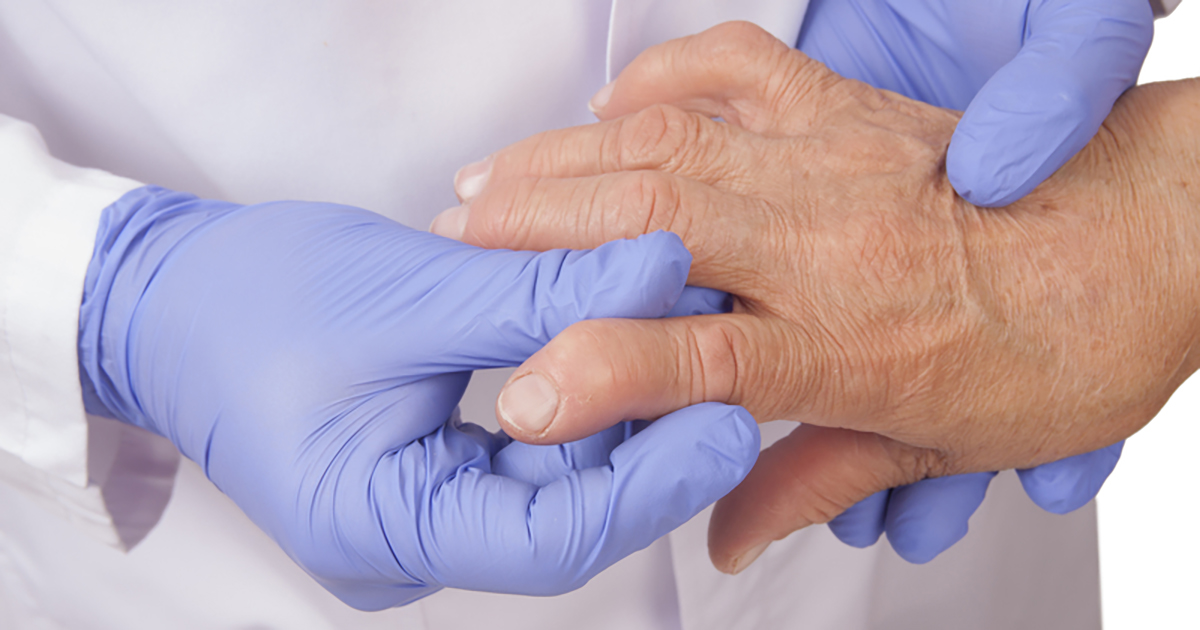
Inflammatory conditions contribute to the development of de Quervain's tenosynovitis in a few diverse ways. The first is through a condition like arthritis, which is an inflammation of one or more joints. Near the thumb, there are many different joints. For example, the distal radioulnar joint is found close to where the extensor pollicis brevis and adductor pollicis longus travel to the thumb. There are also many joints between the carpal bones of the wrist. When these joints become inflamed, they may place too much pressure on the EPB and the APL, making their movement more strained. If this continues for a long time, the condition will become de Quervain's tenosynovitis. Sometimes, the EPB and the APL themselves become inflamed, or the tenosynovium becomes thickened. Both of these will cause the tendons to have a harder time moving, leading to de Quervain's tenosynovitis.
Discover more of the risk factors and causes of de Quervain's tenosynovitis now.