Guide To The Symptoms Of Truncus Arteriosus
Cyanosis
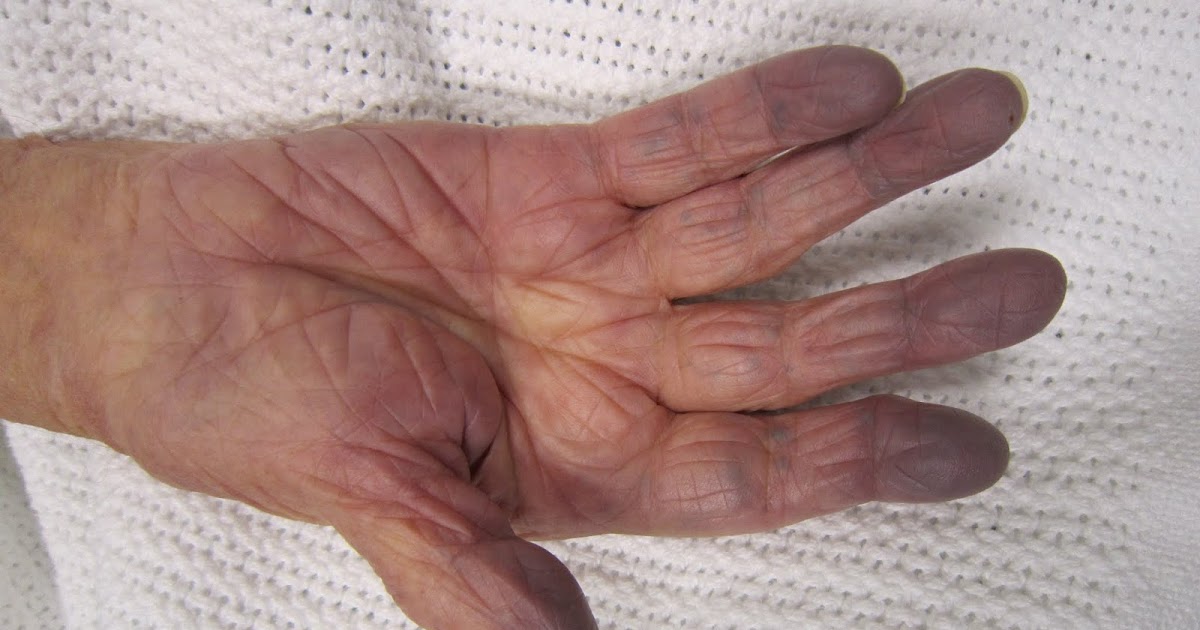
Cyanosis is a condition characterized by low blood oxygen levels that causes a patient's skin to turn blue in several regions of the body. Cyanosis happens when there is a mechanism present that allows the oxygen-poor blood from the right side of the heart into the left side of the heart that should only contain oxygen-rich blood. In individuals affected by truncus arteriosus, a hole is present in the wall between the right and left ventricles. This hole allows the oxygen-poor blood to mix with oxygen-rich blood before it is either sent back into the lungs or out into the rest of the individual's body. As a result, the blood circulating around the body is poorly oxygenated or not oxygenated at all. Oxygen-rich blood is bright red, while oxygen-poor blood is typically dark maroon. Light from outside of the body reflects off the dark red color of oxygen-poor blood in a different way than it does with the bright red oxygen-rich blood. This difference is what makes truncus arteriosus patients have cyanosis.
Get more details on the warning signs of truncus arteriosus now.