How To Effectively Treat Myocarditis
Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation
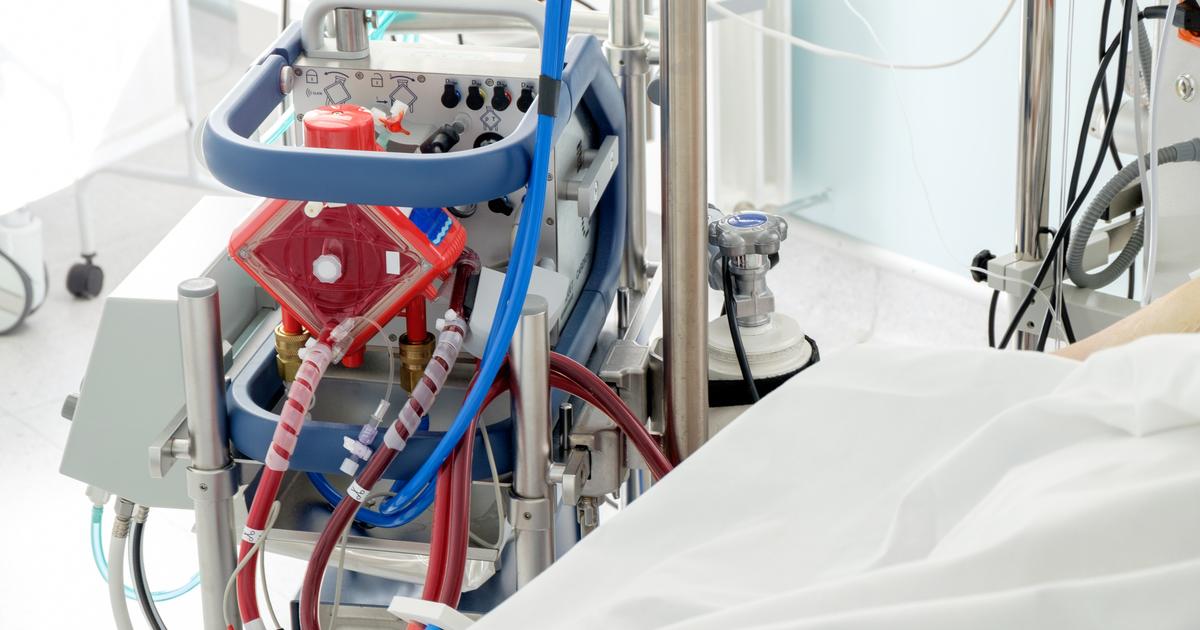
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a way to provide oxygenated blood to the body through the use of an external machine. The ECMO machine works similarly to the bypass machine typically used during open heart surgical procedures. When a patient is on ECMO, their blood is removed from their body and sent into the machine through special tubing. The patient's blood then flows through an artificial lung inside of the machine. The lung extracts carbon dioxide from the blood and infuses oxygen into the blood. The patient's blood is then transported to another part of the ECMO machine that warms it up to the correct body temperature. Once heated, the oxygenated blood can be pumped back into the patient's body. ECMO may be used to stabilize and support patients who have experienced acute heart failure as a complication of myocarditis. It can also be used for myocarditis patients who have suffered permanent heart damage as a bridge to other treatment options like a ventricular assist device. The use of ECMO to temporarily take over the functions of the heart and lungs can accelerate the healing of heart tissues affected by myocarditis.