How To Treat A Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Shunt Placement
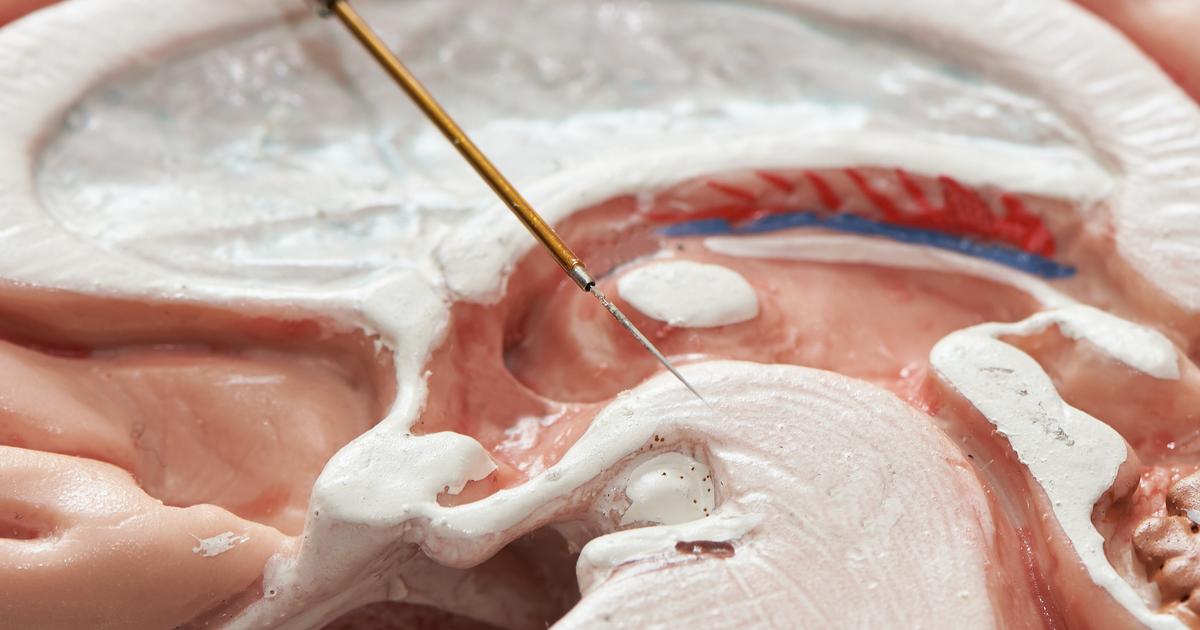
Shunt placement is the more permanent version of external ventricular drain placement. Shunts are hollow tubes placed in the brain or spine by a neurosurgeon. They drain excess cerebrospinal fluid, redirecting it within the body to a place where the body can reabsorb it. A shunt procedure is used to manage hydrocephalus, which can be a complication following a subarachnoid hemorrhage. The procedure is usually used when hydrocephalus cannot be cured or stopped. A permanent shunt is completely internal, unlike an external drain. It helps relieve the symptoms that come with hydrocephalus, including a lack of bladder control, mild dementia, and difficulty with walking. Doctors will sometimes do a lumbar puncture to decide whether the patient is a good candidate for a shunt. If the lumbar puncture improves symptoms, a shunt may provide the same relief.