How Choledocholithiasis Is Treated
The gallbladder is a hollow, sac-like organ that sits just beneath the liver. Its primary function is to store and release bile produced by the liver. When food enters the small intestines, the gallbladder squirts bile through a series of tubes known as ducts into the small intestines, where it helps the digestion of fats. Sometimes, the gallbladder can form gallstones, which refer to solid deposits of cholesterol and other substances in bile. These solid deposits may develop when there is an imbalance in the chemicals that make bile. The gallstones can get stuck inside the gallbladder or in one of the ducts leading to the bowel. Choledocholithiasis is a condition that occurs when the solid deposits block the common bile duct, thus preventing the free flow of bile into the intestines. Instead, the bile backs in the liver and gallbladder. If the obstruction persists, the gallbladder can become inflamed, and the affected individual develops cholecystitis, an acute inflammation of the gallbladder. Get to know the necessary treatments for choledocholithiasis now.
Cholecystectomy
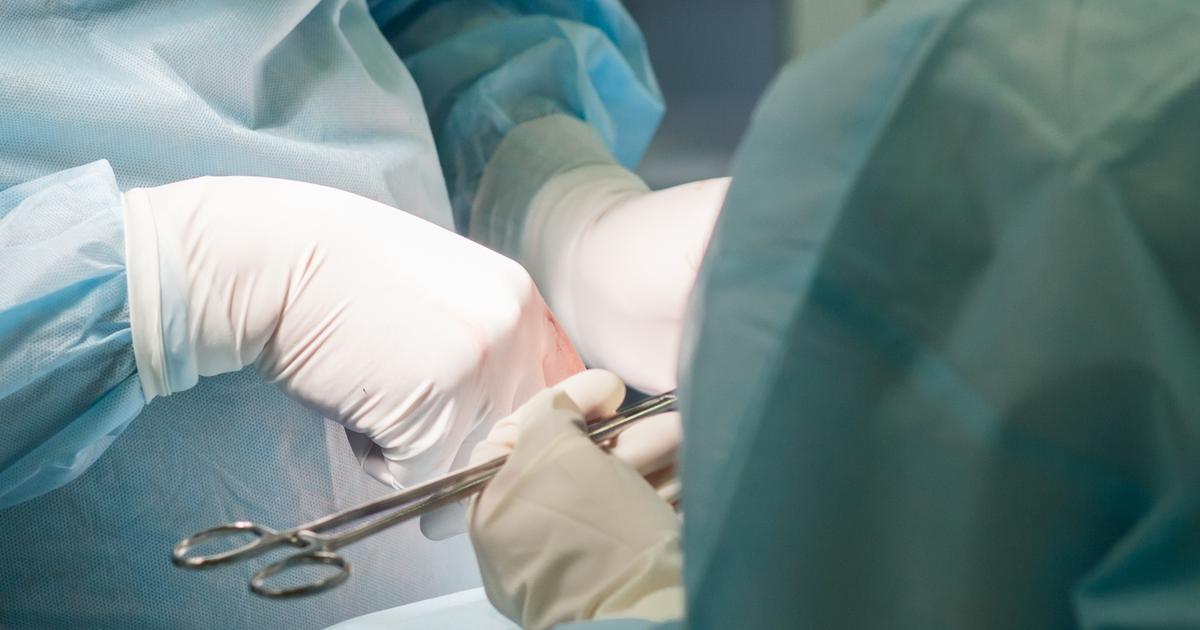
Once gallstones begin forming in a patient's gallbladder and inside the ducts, they usually don’t go away on their own. The only way to stop gallstones from reoccurring is by performing a cholecystectomy, a surgical procedure that leads to the removal of the gallbladder. This is a standard procedure recommended for individuals whose gallstones are symptomatic, and it is considered a minimally invasive procedure with a small risk of complications. The gallbladder can either be removed by conducting an open surgery or through laparoscopic techniques.
In open surgery, the surgeon will make a five- to seven-inch cut on the patient's abdomen to remove the gallbladder. Open surgery is rarely used for the removal of gallbladder unless the patient is extremely overweight, in their last trimester of pregnancy, or if they have a bleeding disorder. During the laparoscopic procedure, the surgeon makes four small incisions on the abdomen where they insert a tiny camera (a laparoscope) and specialized tools to take out the gallbladder. The main benefit of the laparoscopic procedure is the patient does not experience pain during surgery and they can resume their duties immediately.
Keep reading to learn more about how to treat choledocholithiasis now.