Risk Factors And Causes Of Melioidosis
Melioidosis is a potentially life-threatening disease caused by bacteria and can strike both humans and animals. The disease is not common in the United States, but is a problem in parts of Asia, Australia, and other tropical regions of the world. However, it can spread to other places fairly easily. The symptoms of the disease depend on what organs are infected, and the length between exposure to the bacteria and the first symptoms can range from hours to years. Some individuals with melioidosis are asymptomatic. Others have infections in their blood, their lungs, their skin, or in more than one organ. Get to know the risk factors and causes of melioidosis now.
Bacterium Called Burkholderia Pseudomallei
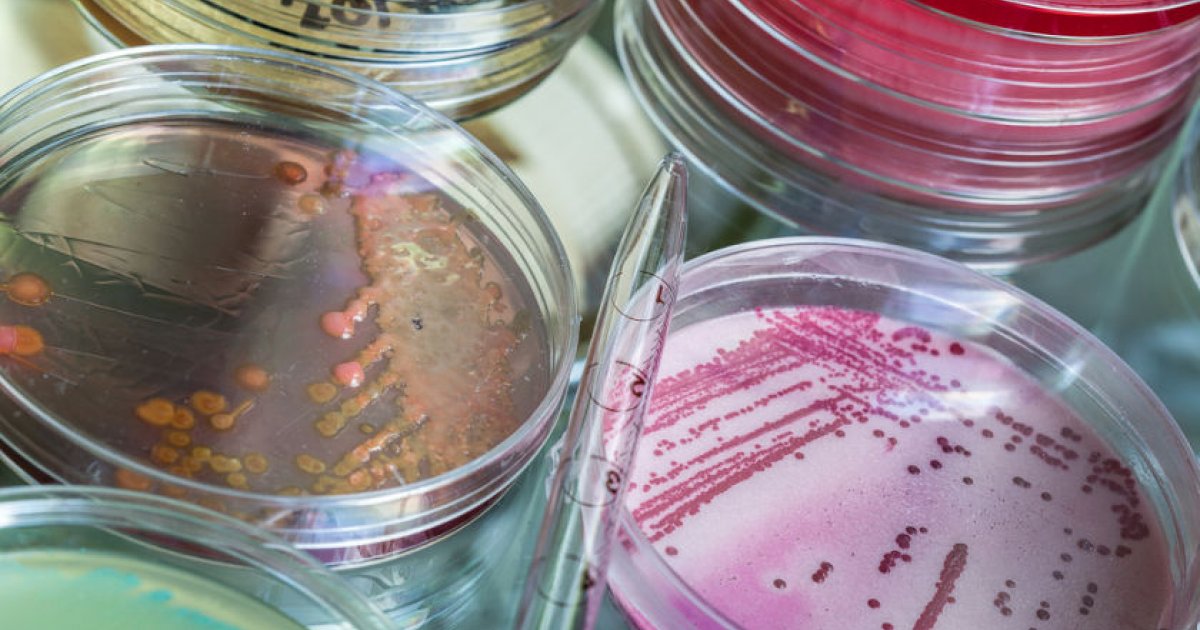
The cause of melioidosis is a bacterium called Burkholderia pseudomallei. It is gram-negative, which means it does not stain the violet color of gram staining and resists some antibiotics. B. pseudomallei is found in water and soil. It is related to a bacteria that causes a disease called glanders in equines, and the name melioidosis is derived from a Greek word that refers to distemper in asses. The bacterium has two poles, lives in an oxygenated environment, and is rod-shaped and can move on its thanks to flagella, or whip-like appendages. It’s about two to five nanometers long and thrives in somewhat acidic or neutral environments in temperatures around 104 degrees Fahrenheit. When it is grown in a petri dish in a lab, B. pseudomallei appears in wrinkled-looking colonies that have the odor of putrefaction.
Learn more about the causes and risk factors of melioidosis now.