Guide To The Causes And Risk Factors For Rhabdomyosarcoma
Neurofibromatosis
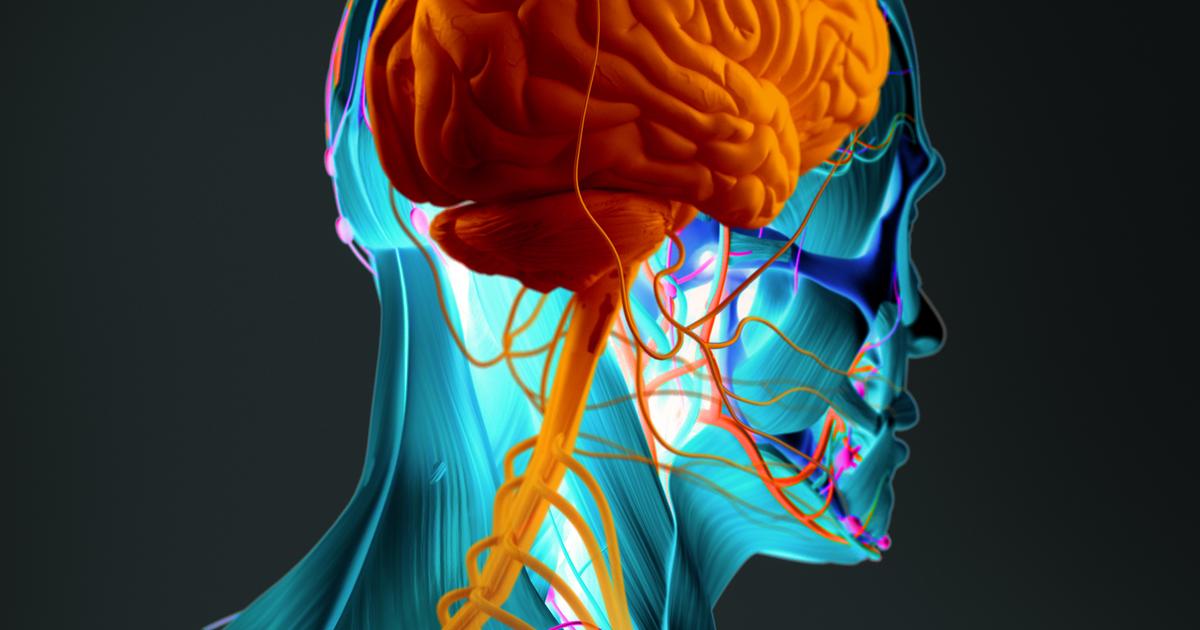
Neurofibromatosis patients are at a higher risk of developing rhabdomyosarcoma as a complication of their disorder. Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that affects the cells that make up the nervous system around the body. Common manifestations of neurofibromatosis include patches of light brown skin, bone deformities, hearing loss, neurofibromas, bone enlargement, scoliosis, and learning disabilities. Neurofibromatosis is caused by mutations in certain genes passed down from a patient's parents in most cases. The mutation that causes neurofibromatosis that occurs on the NF1 gene on chromosome 17 promotes the uncontrolled growth of cells around the body as a result of a deficiency of neurofibromin. The causative mutation that occurs on the NF2 gene on chromosome 22 promotes uncontrolled cell growth in tissues by decreasing the amount of a protein called merlin. The causative mutation that may occur on the SMARCB1 and LZTR1 genes also promotes cell proliferation by reducing the amount of other tumor-suppressing proteins. It is the cell proliferation that occurs in close proximity to soft tissues that cause the development of soft tissue cancers like rhabdomyosarcoma.