Treatment Options For Polycythemia Vera
Polycythemia vera is a type of blood cancer in which the patient’s bone marrow makes too many red blood cells. The patient’s blood thus becomes abnormally thick, and circulation slows. This, in turn, can cause complications like blood clots that can lead to a stroke or heart attack. Polycythemia vera is uncommon. It also develops slowly, so a patient can have it for years without knowing it. In many cases, the doctor will diagnose the condition while performing a blood test for some other reason. While many patients do not show any symptoms, others may develop symptoms such as weight loss, fever, minor bruising or bleeding, fatigue, and itchiness, especially after a warm shower or bath. Polycythemia vera is most common in adults over sixty years old and can be life-threatening if it is left untreated. Treatment options include those described below.
Phlebotomy
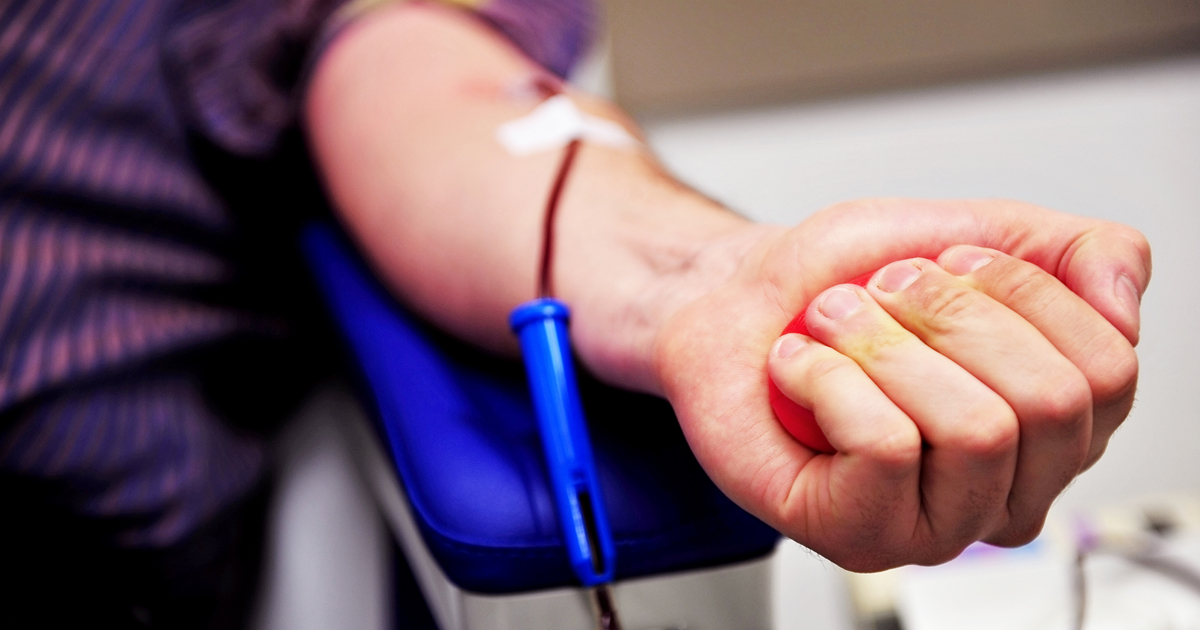
Phlebotomy is usually the first treatment a doctor will try on a patient with polycythemia vera. Also known as 'bloodletting,' it is an ancient practice that dates back centuries. A specialist called a phlebotomist will insert a needle into a vein and draw out the patient’s blood. The process is similar to giving blood, and it can be performed in any clinical setting like a hospital, doctor’s office, or nursing home.
The goal of a phlebotomy is to reduce the number of blood cells and help the blood flow more easily. It can also ease symptoms like dizziness or headaches. The doctor may also draw blood to perform a red blood cell count or another diagnostic test.
Learn more about treating polycythemia vera effectively now.