How To Treat Calcinosis Cutis
Calcinosis cutis is a group of skin disorders characterized by salt crystal accumulation in the skin. This forms hard bumps called calcium deposits that do not dissolve. This results in lesions on the skin of numerous different shapes and sizes. There are five different types of calcinosis cutis. Dystrophic calcification happens due to the initial inflammation and damage done to the skin and is the most prevalent type of calcinosis cutis. Metastatic calcification is caused by abnormally elevated phosphorus and calcium levels in the body. Idiopathic calcification usually happens in a localized region of the body and has no defined cause. Latrogenic calcification happens as a result of medical therapy or a medical procedure that causes some type of skin damage. The last and most serious variation of calcinosis cutis is calciphylaxis, which is a result of abnormal phosphate and calcium levels in the body. Most patients diagnosed with calciphylaxis are in a stage of kidney failure, on dialysis, or have received a kidney transplant.
The treatment recommended for calcinosis cutis is dependent upon what underlying disease or cause is present.
Surgical Intervention
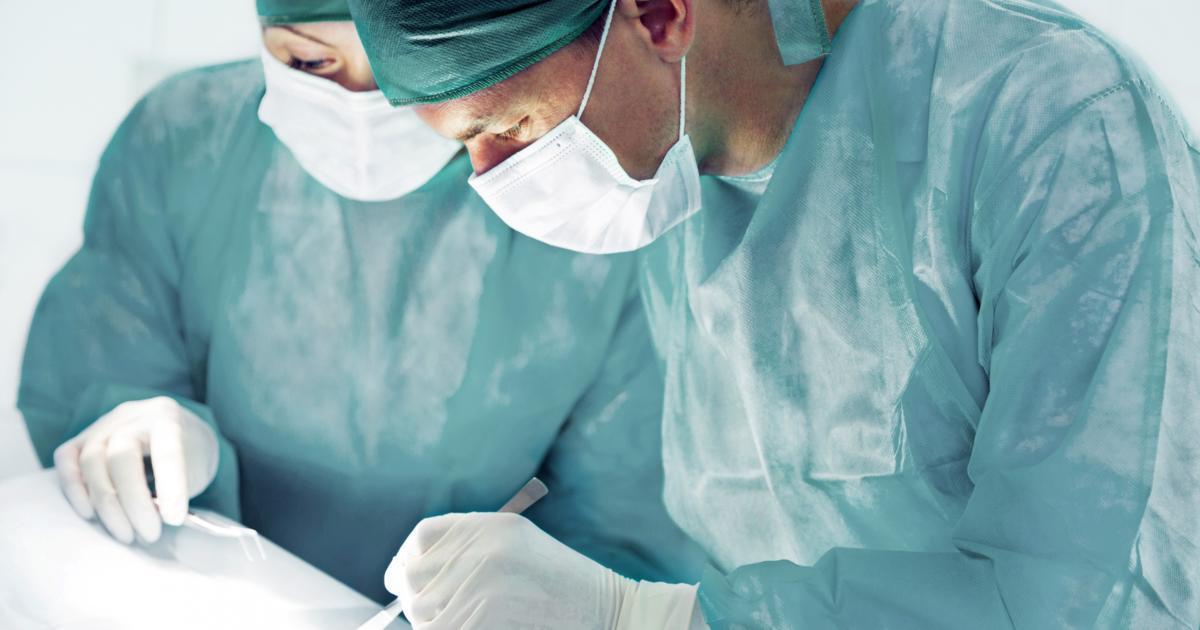
Surgical intervention when referring to calcinosis cutis involves the lesions being surgically removed from the skin. The white calcium deposits can develop in clusters or grow to become a large size. Most often these lesions form on the front of the legs, elbows, and fingertips. When lesions form in sensitive areas like the joints, they have the capacity to cause pain. They can also ulcerate, or split open, leaving the skin susceptible to bacterial invasion. Additionally, they can impair the normal functioning of other body parts and pose a challenge to individuals who have them in their daily activities. When the lesions become problematic in any of these ways, surgical intervention or removal may be recommended. Because calcification in the skin can be triggered by trauma to the skin due to a surgical procedure, usually a small test excision is performed before the large scale removal of problematic lesions. This is done to ensure the patient is not sensitive to the surgery and to ensure there is no post-excision recurrence.
Learn more about treating calcinosis cutis effectively now.
Medications Available

Medications that can be utilized to help treat calcinosis cutis typically depends on the underlying cause. In patients who have hyperphosphatemia, which causes the lesions, aluminum antacids and magnesium may be able to neutralize the high phosphate level in the blood. This stops the formation of skin lesions. Calcium blocker medications are also prescribed to treat calcium deposits because they decrease the quantity of calcium the skin cells can absorb. Amlodipine, verapamil, and diltiazem are the most prevalent calcium blockers utilized for this purpose. Other anti-inflammatory and steroid medications such as colchicine, warfarin, and prednisone are also prescribed to assist with shrinking lesion deposits. Medications such as diphosphonates and sodium etidronate are also effective agents for inhibiting the growth of calcifications in soft tissue with ongoing treatment. Any medications that help treat the underlying causes of the calcium crystal formation are also imperative to the treatment of calcinosis cutis.
Uncover the next option for treating calcinosis cutis now.
Lithotripsy
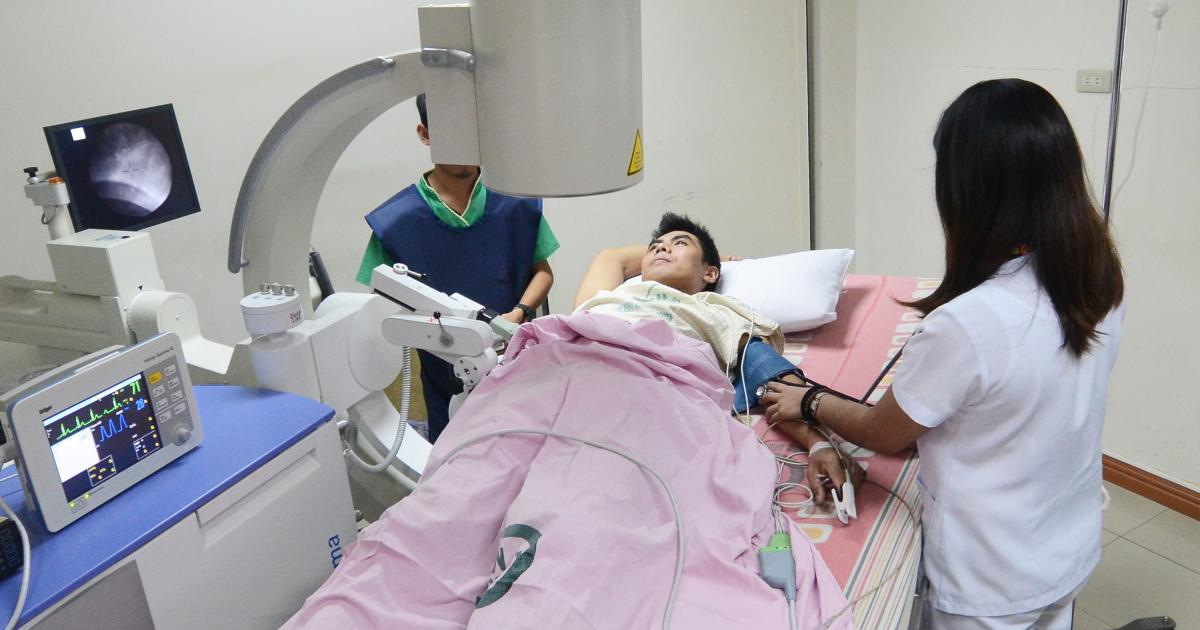
Lithotripsy is a treatment mainly used to treat certain types of stones in the kidneys, bladder, and other organs. Often times these stones are made of the same materials as those that occur in calcinosis cutis. This type of treatment effectively breaks these stones up into smaller pieces by utilizing sound waves or high-energy shock waves. These types of waves also do not pose any harm to skin, bone, or muscle. Lithotripsy is typically used as a pain management measure for individuals with especially complex cases of calcinosis cutis. In some circumstances, this type of therapy is used to break up the stones before surgical deposit removal. The purpose of doing so is to make the surgical removal of the deposits quicker, easier, and less invasive. Minimal invasion when it comes to surgical removal of deposits is an important factor to take into consideration because surgical trauma can trigger calcinosis cutis single-handedly.
Continue reading to reveal more treatments for calcinosis cutis now.
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is a treatment that utilizes allogenic or autologous stem cells to repair a patient's defective or damaged immune system. This is done by matching an appropriate donor to the recipient and then using intravenous means to infuse the patient with stem cells. While calcinosis cutis is not an autoimmune disorder itself, it is closely associated with autoimmune disorders like systemic lupus, dermatomyositis, systemic sclerosis, mixed connective tissue disease, undifferentiated connective tissue disease, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis, and overlap connective tissue disease. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is an effective treatment for several of these diseases and numerous variants of them. By treating the underlying disease triggering the development of calcium deposits in the skin with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, the symptoms and outbreaks of calcinosis cutis should significantly decrease in severity and frequency.
Get the details on more options to treat calcinosis cutis now.
Laser Therapy

Laser therapy is used to treat various connective tissue disorders including dermatomyositis, which is characterized by lesions all over the body that become immune or resistant to other types of treatment. Calcinosis cutis is a difficult complication that can occur with dermatomyositis and numerous other similar connective tissue disorders, all of which can lead to intense pain, infection, and tissue damage if they are not treated. One of the newer emerging methods of treating the calcium deposit lesions on the skin that result from dermatomyositis and calcinosis cutis is the use of a carbon dioxide laser. A carbon dioxide laser is utilized to help remove the deposits with better precision, limited blood loss, and faster healing processes. Laser CO2 therapy allows lesions to be removed in a safer and less invasive manner than a traditional surgical excision. The very short-pulsed or ultra-pulsed light beams or light energy are applied to the lesion in a scanning mannerism or pattern. Very minimal damage occurs to the surrounding areas of skin and the risk of complications is much lower with CO2 laser therapy than it is with traditional calcium lesion removal.