Causes And Risk Factors Of Age Spots
Age spots are blemishes or lesions caused by increased pigmentation due to sun damage or other sources of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. They usually appear on areas exposed to the sun like the face, neck, hands, shoulders, and upper back. Age spots can range in color from grey to black, but they're usually a shade of brown. Age spots are also referred to as liver spots or sunspots. The medical term for this type of blemish is solar lentigo, lentigine, or actinic keratosis. They're common among middle-aged and older individuals, which is why they're called age spots. These blemishes are harmless and can be treated with a variety of methods like skin-bleaching products. Individuals can decrease their risk of age spots by limiting their exposure to the sun and using a broad-spectrum sunscreen. They can also protect themselves by covering up with clothing, eyewear, and a hat.
Get to know some significant risk factors and causes of age spots now.
Overactive Pigment Cells
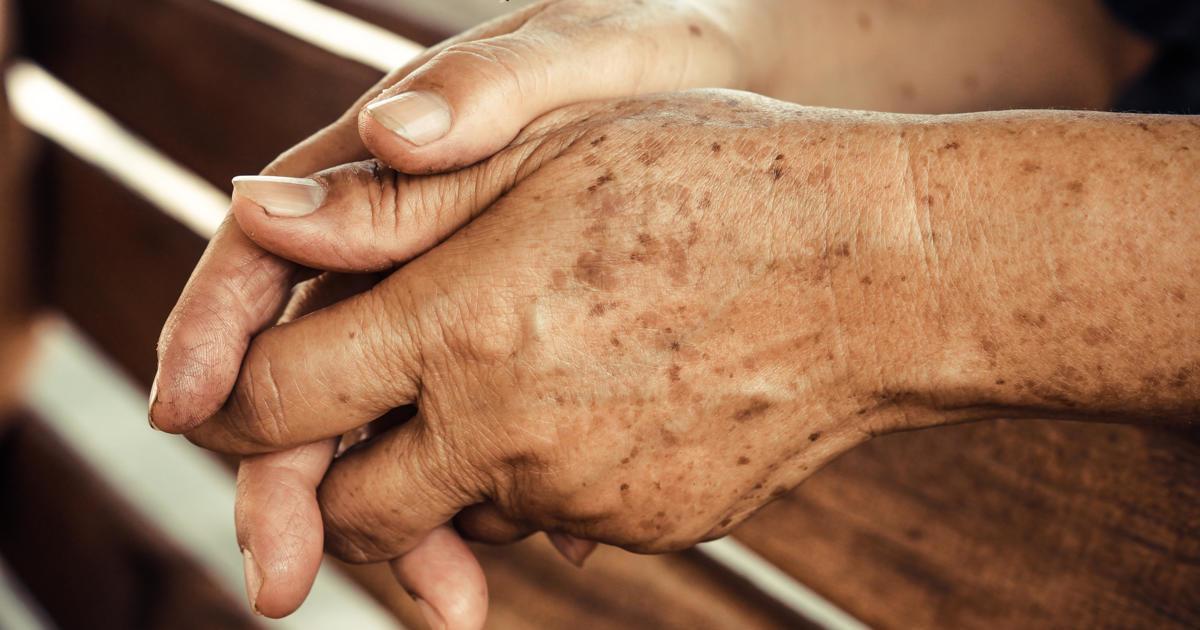

The production of melanin is a normal process in most organisms. Melanin is the pigment that produces the many colors in our skin and hair, and also protects it from the sun. The light from the sun hastens the production of melanin. This brings about high concentrations and clusters of the pigment in certain areas of the body, which are typically those exposed to the sun for extended periods. The surge in activity of the pigment cells produces extra melanin, causing age spots to appear on the skin. These small areas will darken and remain on the skin unless lightened or removed by other methods. The extra pigmentation that develops from overactive pigment cells is stronger in individuals with darker skin tones, but it's naturally more evident in those with lighter complexions.
Keep reading to reveal more on how the sun triggers age spots.
Prolonged Sun Exposure
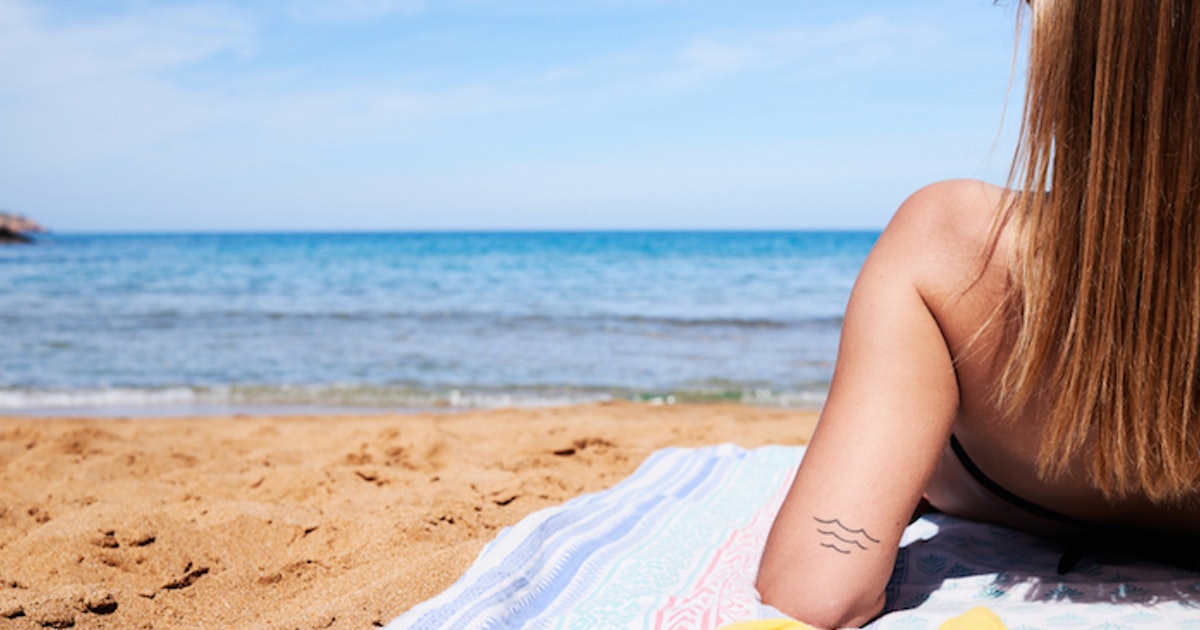

The main cause of age spots is prolonged sun exposure, so it's essential for individuals to limit their time in the sun. Many individuals are sun worshippers and love to spend time working on their tan or just soaking up its rays. The glow of a suntan and the warm, enticing rays of the sun may be appealing, but the long-term effects of this exposure can be harmful to the skin and overall health. Prolonged sun exposure can cause age spots and lead to signs of premature aging like wrinkles. It also increases an individual's risk of developing skin cancer. Protecting skin from the sun can add years of life regarding its health and appearance. Individuals who spend too much time in the sun may experience many more instances of age spots and other ill effects in comparison to those who avoid the sun.
Get details on how tanning can influence age spots next.
Tanning Lamps And Beds
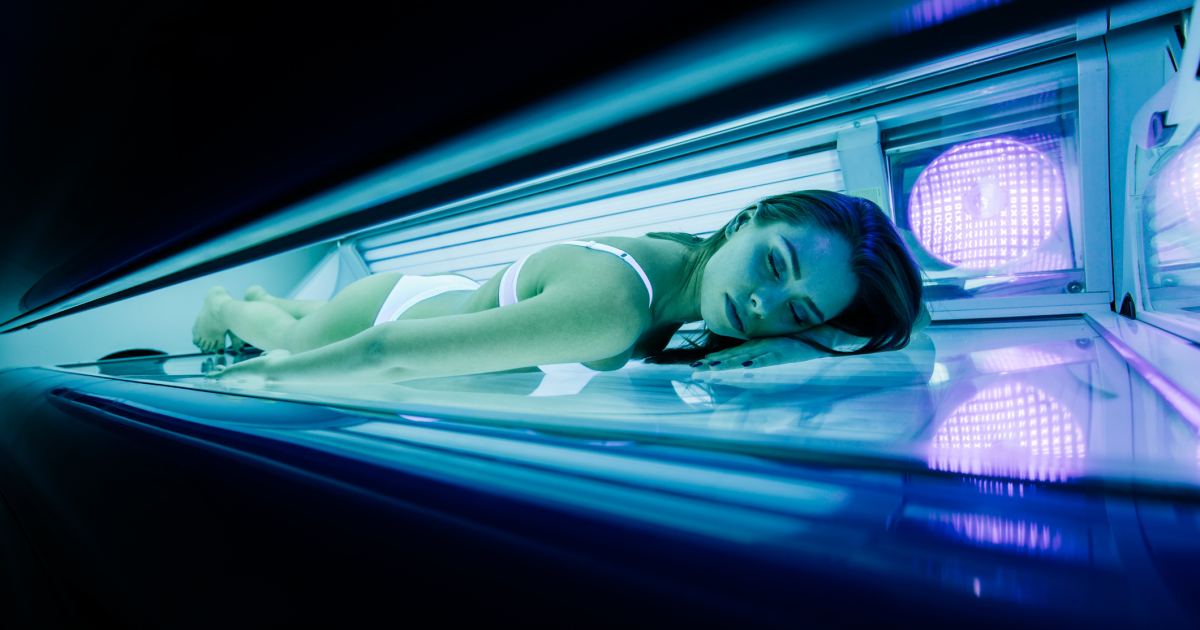

The use of tanning lamps and beds over a long period can cause age spots to develop because of the continuous exposure to UV rays. These rays can cause damage to the skin and lead to various forms of skin cancer. Indoor tanning is very popular among young individuals and many start using tanning lamps and beds during adolescence and early adulthood. Also, these individuals may use tanning equipment more frequently and increase their risk of sun damage such as wrinkles and age spots. The use of this equipment can cause many years worth of sun damage prematurely, especially for frequent users. Tanning beds emit UVA rays, which are more dangerous because they penetrate deeper into the skin. Age spots caused by sunshine are usually due to UVB rays and typically affect the top layers of the skin. Skin damage from tanning beds can cause much more extensive damaging changes in the skin.
Get to know a major risk factor for age spots related to an individual's appearance next.
Red Hair And Light Skin
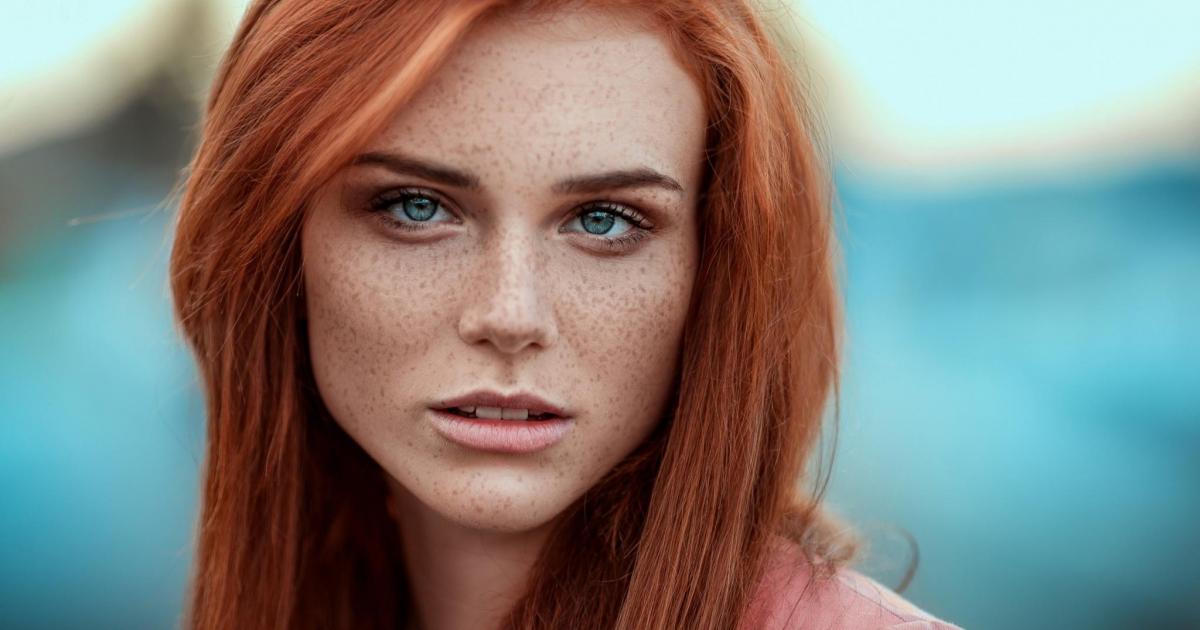

Individuals with red hair and light skin have a higher risk of age spots and other damage from ultraviolet light because they have less melanin available for protection against sun damage. Redheads have an increased risk of sun damage because of their genetics. The same gene that causes their red hair contains a mutation that also interrupts communication between the skin cells responsible for protecting itself from UV radiation. Individuals with red hair and light skin are more likely to develop age spots and other blemishes like freckles because of their pigment pattern and the miscommunication of their melanin-forming cells. Redheads and those with light skin tones are also more vulnerable to getting sunburned faster than the rest of the population.
Learn more about the various risk factors of age spots now.
History Of Intense Sunburns
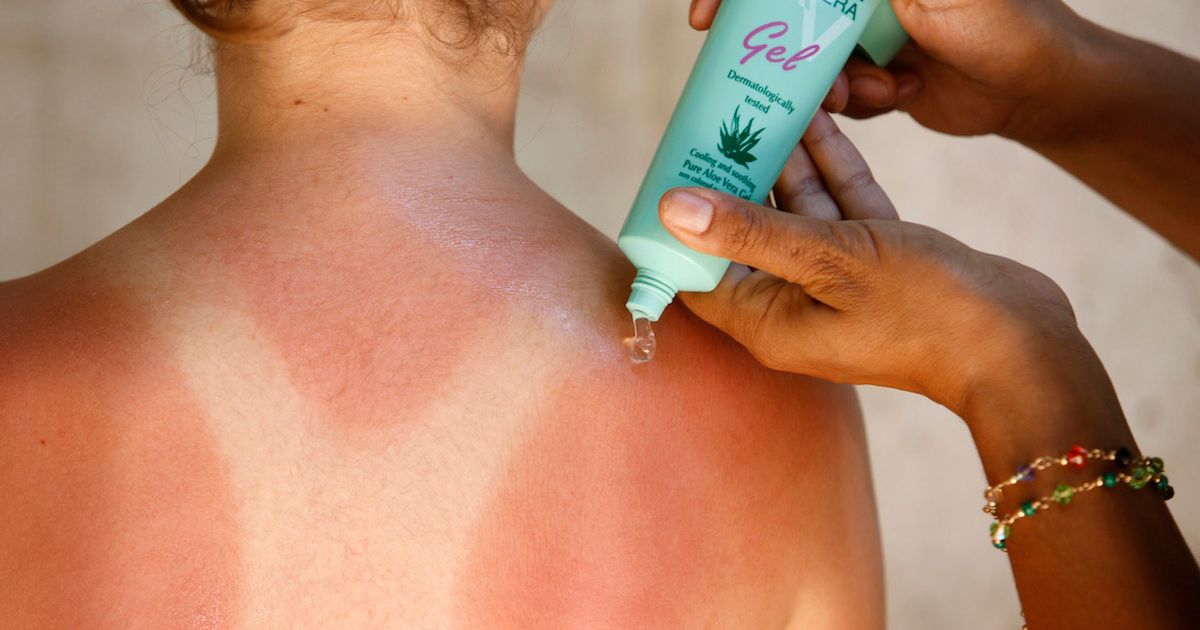

Individuals with a history of intense sunburns tend to prematurely develop age spots and other damage to the skin like freckles and wrinkles. Those individuals who experience five or more intense sunburns by twenty years old are at an increased risk of developing age spots and skin cancer. A history of sunburns that can be classified as second-degree burns or worse may cause age spots to appear prematurely. Ultraviolet radiation causes damage to the skin's collagen and elastin, which can leave the skin looking saggy or leathery and littered with the brown patches known as age spots. All it takes is one bad sunburn for age spots to appear, but a history of intense sunburns can drastically increase their occurrence and amount.
Read more about risk factors and causes associated with age spots now.
Advanced Age

Advanced age is one of the major risk factors for age spots, and they are very common in adults over fifty years old. Many of these individuals will have several age spots. However, these spots can begin appearing at forty years old, and some individuals may even develop age spots in their teenage years. As individuals age, they typically accumulate more exposure to the sun and other sources of ultraviolet rays, and this ultraviolet exposure causes the formation of the spots. Since age also increases the risk of other skin conditions, including melanoma and other forms of skin cancer, patients should see a dermatologist for a yearly skin examination. This is especially important since certain skin cancers often appear very similar to age spots.
Get more details on causes and risk factors of age spots now.
Previously Believed To Be Caused By Liver Problems

Age spots were previously believed to be caused by liver problems, which is why some referred to them as liver spots. However, scientists now recognize these spots have absolutely nothing to do with the liver at all, and they are not indicative of any liver concerns. Known as lentigines, the spots are simply localized concentrations or clumps of a pigment called melanin. As mentioned, patients who have light skin and red hair are believed to be at a greater risk of developing lentigines, and individuals who have previously been sunburned are also at an increased risk.
To prevent these spots, doctors recommend patients stay out of the sun as much as possible, and tanning beds should not be used. Sunscreen should be worn at all times when outdoors, even if it is a cloudy day, and patients may wish to wear clothing specially treated to provide built-in sun protection. Dermatologists recommend that patients avoid sun exposure during the afternoon hours as the sun's rays are particularly intense during this time. Age spots can be lightened with prescription retinol products, and laser treatments, chemical peels, freezing procedures, and surgical options are available to remove the spots entirely.
Learn more about age spots now.
Location And Appearance
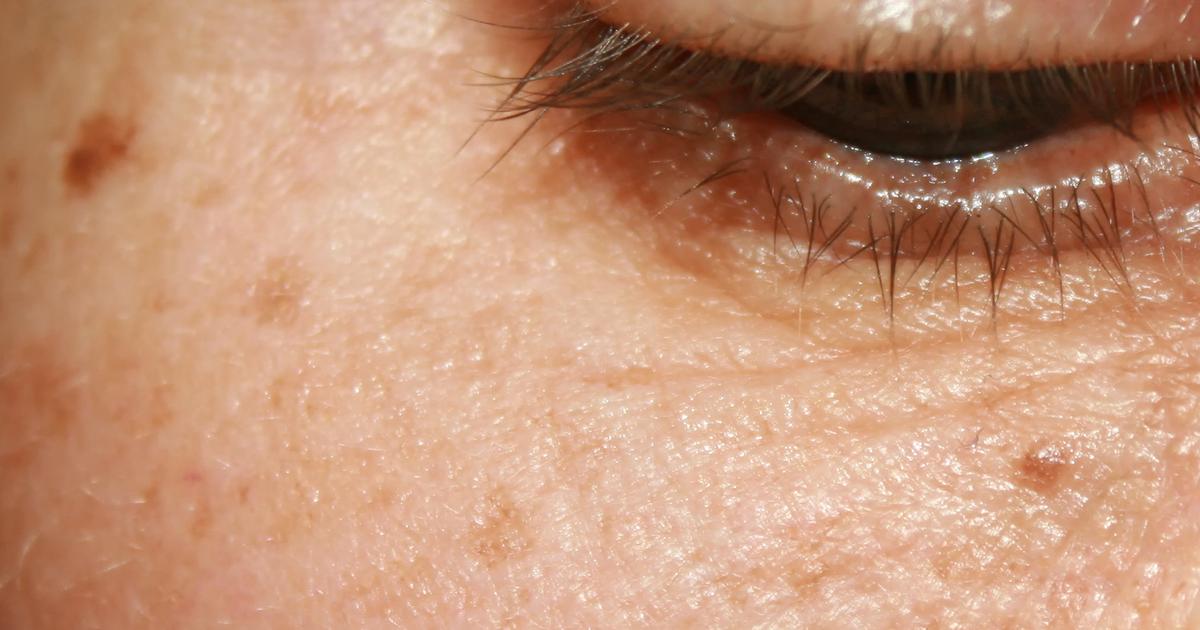
Age spots may develop anywhere on the body, though they appear most frequently in areas that have experienced the highest amounts of sun exposure, including the face, feet, shoulders, and upper back. Patients may also develop them on the backs of the hands and on the forearms, and they could appear on the upper chest as well. It is common for clusters of several small age spots to appear on the skin. These spots tend to be tan, brown, or black, and they might sometimes be gray. These spots are universally flat and round or oval in appearance; they are never elevated (raised above the surface of the skin). In terms of texture, the spots will almost always have an identical texture to the surrounding skin. At times, they may be slightly rough. The average size of an age spot ranges from 0.2 centimeters to two centimeters in diameter. Patients should monitor their skin for any new spots. If a new or existing spot bleeds, changes color, elevates above the skin, or increases in size, an evaluation should be conducted by a dermatologist. Any spot that is flaky, red, itchy, or painful warrants a medical examination too.