What Are The Causes And Complications Of Urinary Incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is a condition that occurs when an individual experiences a loss of control over their bladder, leading to the involuntary leakage of urine. Some patients with urinary incontinence only experience mild leakage, while others might have a moderate to full loss of their bladder control. This problem is common, but it can be embarrassing. Some individuals leak urine when they sneeze or cough, which is one of the more mild ways the condition can manifest. For others, the urge to urinate becomes so strong and sudden that they can't reach a toilet in time. Urinary incontinence is more common in older individuals, but it can occur at any age. For patients who experience urinary incontinence that affects their day-to-day life, talking to a doctor is the first step to managing it.
Read about the causes and complications of urinary incontinence now.
Carbonated Beverages And Caffeine

Some forms of urinary incontinence occur only temporarily. Rather than being a medical condition that continues during day-to-day life, these types of urinary incontinence can be caused by digesting certain beverages or foods. Caffeine and carbonated beverages can both act as diuretics, which cause the body to release more water and fluid through the bladder. Several other foods and drinks that can have the same effect, such as sparkling water, alcohol, chili peppers, chocolate, citrus fruits, and any other foods that are high in acid and spice. A diuretic stimulates the digestive system and bladder, causing the body to create a larger volume of urine than it usually does, which then leads to the walls of the bladder becoming full and strained. Individuals might experience a more urgent need to use the bathroom, or might need to go to the bathroom several times rather than just once. If individuals think caffeine might be contributing to their urinary incontinence, they should try cutting back for a bit and see if it helps.
Uncover more causes of urinary incontinence now.
Certain Medications

Certain medications can also act as diuretics that stimulate the walls of the bladder and increase urine production. While this is usually the main point of the medication, it can come with the side effect of some urinary incontinence. Some patients experience high blood pressure because the amount of fluid in their bodies causes a narrowing in the blood vessel walls. To combat this, blood pressure medications help the body purge excess fluid and reduce pressure on the walls. The excess fluid is removed from the body through the bladder in the form of urine. Many cardiovascular medications are made to function as diuretics, though they may have other effects as well. Another type of medication that might cause urinary incontinence is a muscle relaxant. Muscle relaxants, as the name implies, relax the muscles throughout the body. This can be extremely helpful in treating spasticity and other conditions, but it can also cause the muscles controlling the bladder to become weaker, leading to leakage.
Uncover more potential causes of urinary incontinence now.
Urinary Tract Infection

Sometimes temporary urinary incontinence is caused by a medical condition that can be easily treated and cured. One of the most common causes is a urinary tract infection. When the infection irritates the bladder, individuals might experience strong and sudden urges to urinate. They might need to go to the bathroom more times than usual and have trouble holding their urine. Some patients experience these symptoms severely enough for it to lead to incontinence. Urinary tract infections can develop in any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys. The majority of these infections involve the urethra and bladder. Urinary tract infections are usually treated with a course of antibiotics. Patients should make sure to take the entire course of antibiotics, as stopping in the middle of treatment can cause the bacteria to recur and become antibiotic-resistant. Urinary incontinence, particularly when it's persistent or recurrent, also increases an individual's risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
Keep reading to reveal more causes of urinary incontinence now.
Menopause

There have been multiple studies indicating menopause is a key factor in the development of persistent urinary incontinence. Not every menopausal woman will develop urinary incontinence, but the chances of developing the condition after menopause become significantly higher than they were before menopause. This is because estrogen plays a key role in keeping the lining of the urethra and bladder healthy. Following menopause, women produce less estrogen. If the tissues lining the urethra and bladder begin to deteriorate, this can make existing incontinence worse. It can also lead to the development of incontinence in women who hadn't previously experienced it. Deterioration of the tissues might also make women more likely to contract a urinary tract infection, which in turn can cause incontinence. This also ties into some of the natural changes that occur during the aging process. Menopause typically occurs in women around fifty years old. At the same time, the bladder muscle's aging can cause a decreased capacity for urine storage.
Read more about what can trigger urinary incontinence now.
Enlarged Prostate
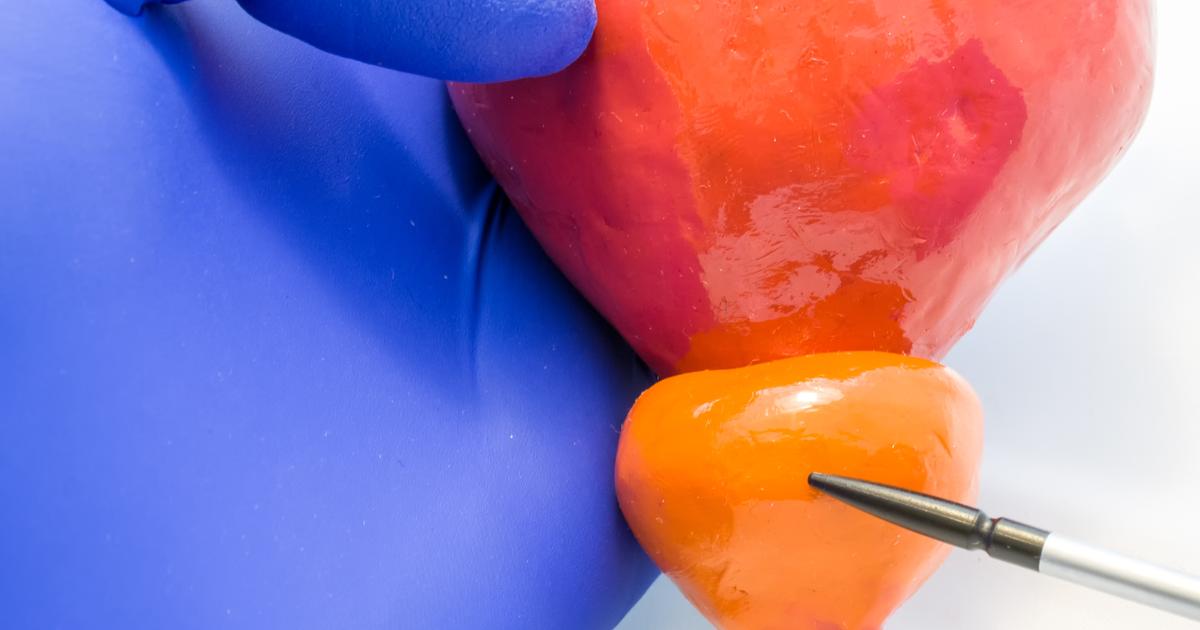
An enlarged prostate is often to blame for urinary incontinence, particularly in older men who experience persistent urinary incontinence. An enlarged prostate, called benign prostatic hyperplasia, can affect anyone who has a prostate gland. It's not always a cause for concern, but it can be an indicator the patients should be checked for prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence has been linked to untreated prostate cancer in some men. It can also occur as a side effect of the treatments men undergo for prostate cancer. An enlarged prostate gland can sometimes cause other uncomfortable urinary-related symptoms as well. One example would be the blockage of urine flow out of the bladder. Some men experience problems with their kidneys or urinary tract in addition to bladder issues. Multiple effective treatments are available for an enlarged prostate, including surgeries, medications, and minimally invasive therapeutic techniques.