Warning Signs Of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus, a poxvirus. This virus produces harmless raised bumps on an individual's upper skin layers that usually do not cause pain. An individual gets Molluscum contagiosum by coming in direct contact with someone who is infected or with a contaminated object. Individuals who engage in sexual contact, play contact sports, and use someone else's personal items or equipment are at a higher risk of contracting Molluscum contagiosum. Diagnosis of Molluscum contagiosum is made with the use of a physical examination and a skin biopsy. Individuals who have a healthy immune system affected by Molluscum contagiosum do not usually require treatment. Cases that do require treatment include when the bumps are on the face and neck, the patient has a preexisting skin disease, or when there is serious concern regarding the spread of the virus.
Read about the major warning signs of Molluscum contagiosum now.
Raised And Flesh Colored Bumps
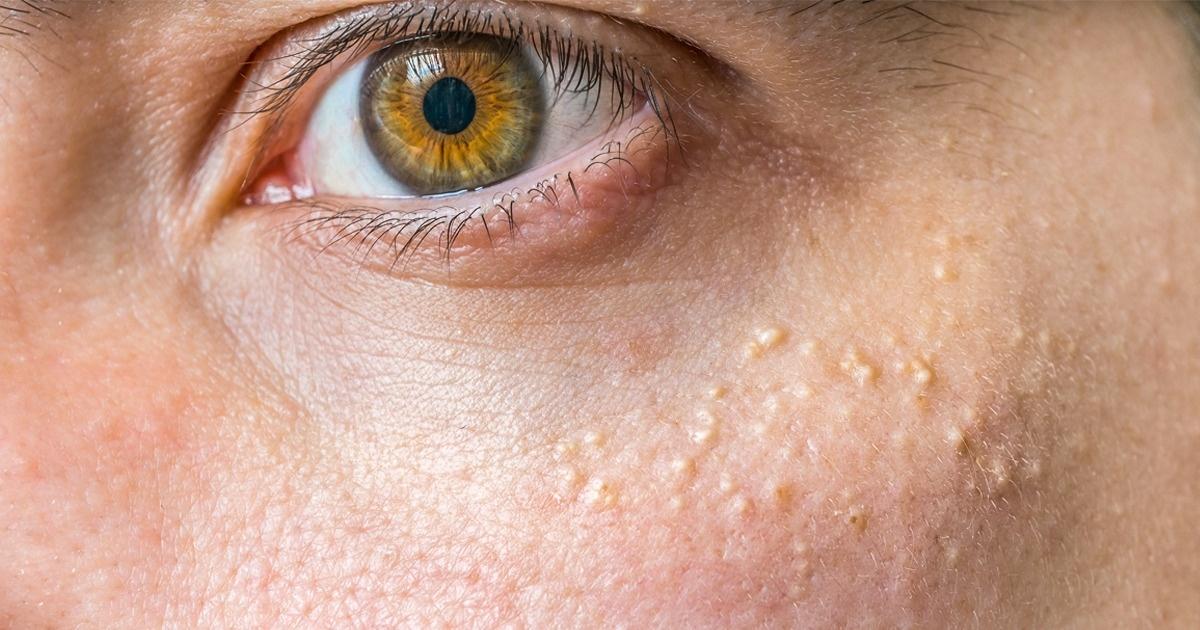
An individual affected by Molluscum contagiosum may develop bumps on their skin that are raised and flesh-colored. The bumps are often referred to as molluscum bodies, condyloma subcutaneous, and Mollusca. They tend to have a dome-like shape, making them palpable and raised compared to the surface of the rest of the skin. Many patients affected by Molluscum contagiosum have described the characteristic bumps that develop on their skin to be wart-like and pearly. The flesh-colored bumps have an average measurement of between two and five millimeters in diameter. These flesh-colored bumps are more common in the beginning stages of molluscum contagiosum, and they start off with a firm consistency. Over time, these flesh-colored bumps become softer and may incur signs of irritation.
Continue reading to learn more about the symptoms linked to Molluscum contagiosum now.
Itchiness
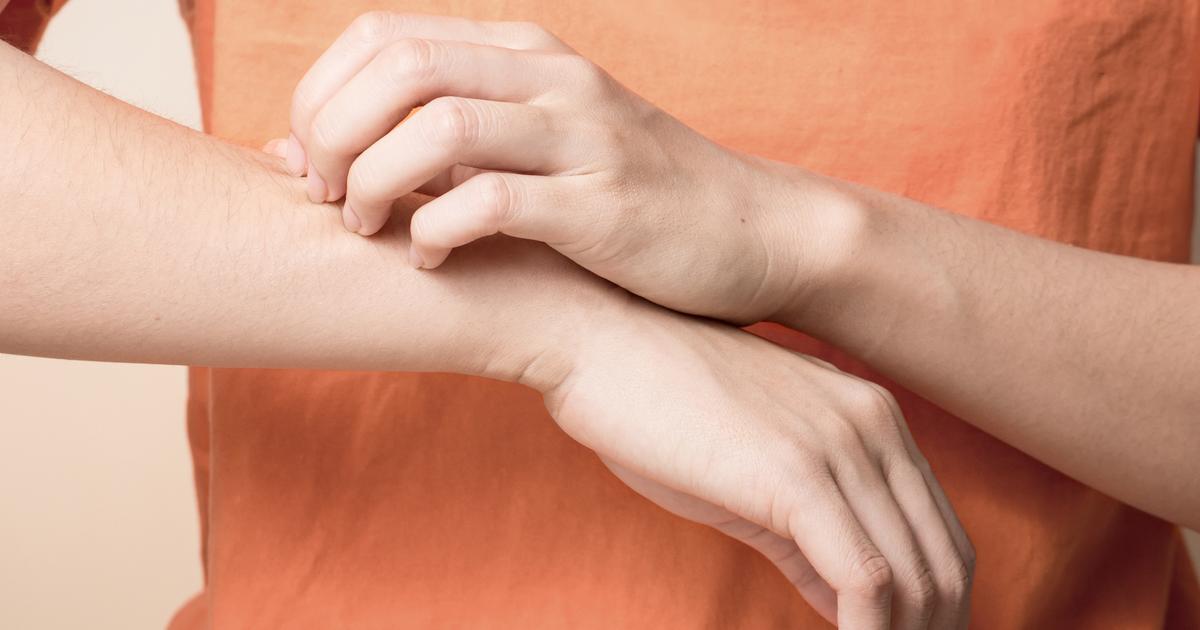

A Molluscum contagiosum patient may experience itchiness, though this is not common during the beginning stages of the infection. As the infection progresses, an individual can experience roughness, pinkness, and itchiness of the skin that surrounds the bumps caused by the virus. This itchiness around the bumps is reported to be similar to the symptoms that occur in an individual affected by eczema. This type of skin reaction that occurs around the molluscum bodies can cause patients to rub and itch the area. If the affected individual scratches or rubs the irritated skin, the virus can spread to parts of neighboring skin as well. A topical medication containing steroids has shown to be effective at relieving itchiness that occurs due to Molluscum contagiosum.
Uncover more warning signs of Molluscum contagiosum now.
Red And Inflamed Bumps

An individual who has red and inflamed bumps on their skin in certain spots may be affected by molluscum contagiosum. The skin lesions that develop in an individual who is affected by molluscum contagiosum tend to start off as painless and don’t cause much physical discomfort for the first couple of weeks. However, the bumps can progress and become red, swollen, and inflamed after that period. The inflammation of any tissues in the body occurs when the immune system reacts to foreign substances, damage to the cells, and harmful pathogens. Molluscum contagiosum is an infection that is caused by a virus that the body sees as harmful, so the immune system jumps into action when the rash on the skin breaks out. It can take days or weeks for the immune system to produce full-blown inflammation in the bumps on the skin. The red and inflamed bumps may ooze pus and may resemble small pimples.
Get more details on the warning signs associated with Molluscum contagiosum now.
Small And Indented Bumps
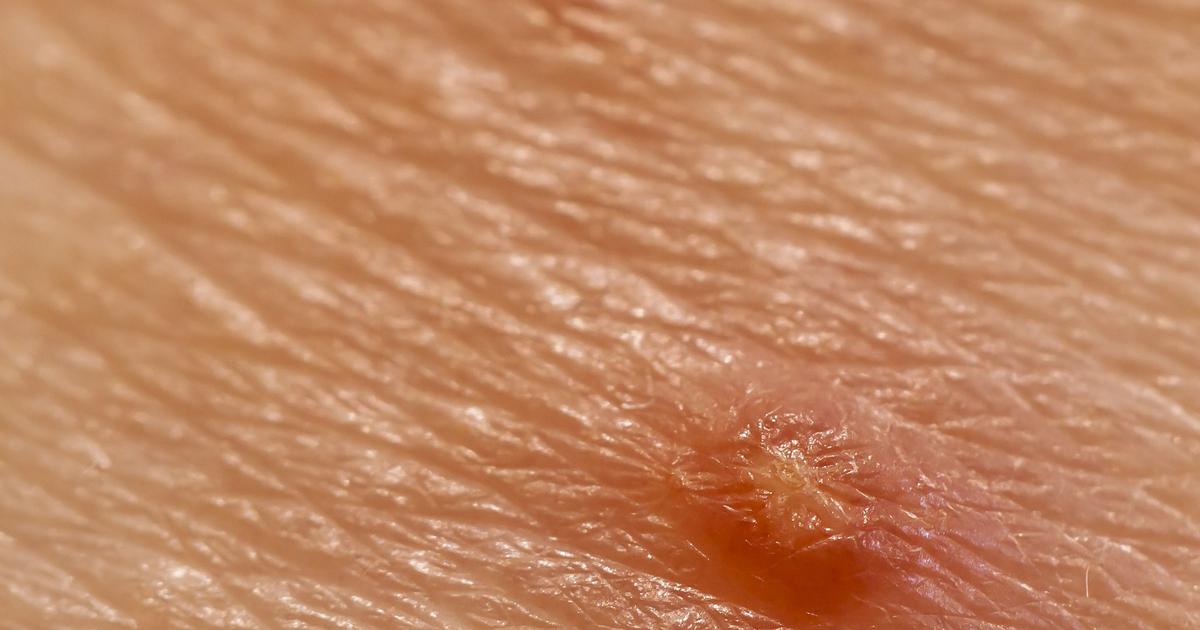
An individual who develops small and indented bumps on certain areas of their skin may be affected by Molluscum contagiosum. In the first few weeks after the molluscum bodies appear on the skin, they are usually very small, flesh-colored, and firm to the touch. Over time the bumps on the skin may become soft in the middle. This change in texture can cause the bumps from Molluscum contagiosum to develop an indent in the center. Some individuals have described the indent that develops as looking similar to a dimple. The papules on the skin of a Molluscum contagiosum patient have also been described as having a volcano shape due to the small indentation on the top of the papules. Some patients only develop bumps on the skin that are round and smooth, which never form an indentation. However, the characteristic dimple in the center of molluscum bodies appears in a large population of affected individuals.
Discover additional symptoms linked to Molluscum contagiosum now.
Location Of Bumps
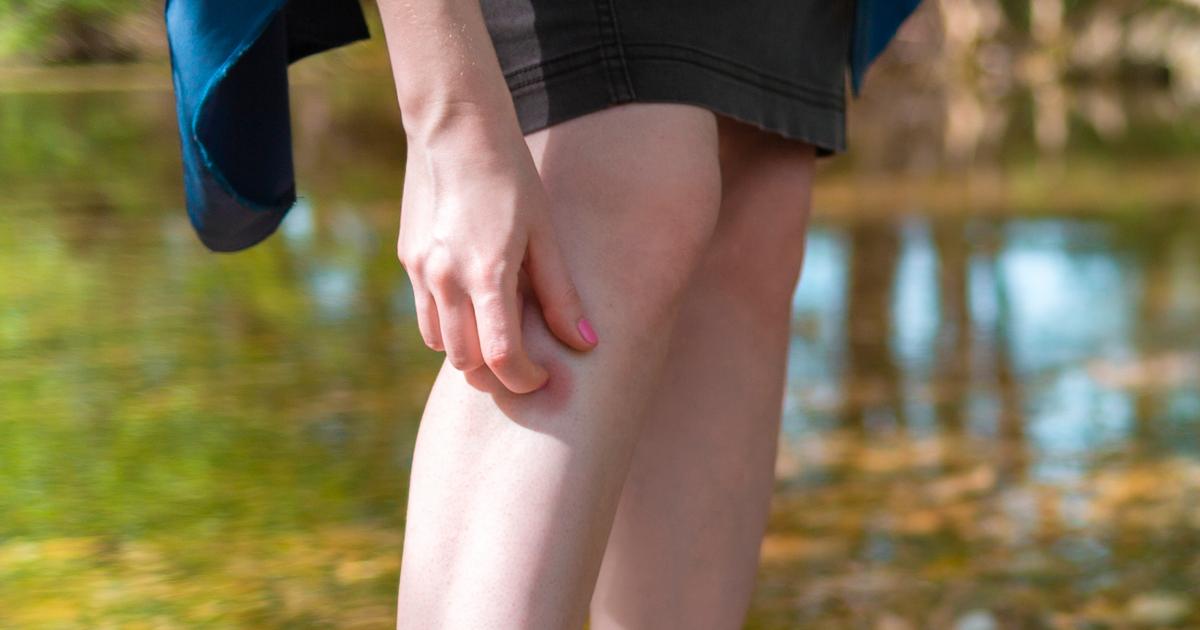
An individual affected by Molluscum contagiosum can develop characteristic bumps anywhere on the skin. The most prevalent areas of the body affected by the bumps are the legs, arms, and trunk. Some patients may experience the development of the molluscum bodies on their neck and face in small groups. Children affected by Molluscum contagiosum tend to develop molluscum bodies on their stomach, face, legs, and arms due to the sharing of toys and other objects where the virus can live. The molluscum bodies can develop in the genital areas of teens and adults that are sexually active. It is also common to see molluscum bodies develop on an individual's inner thigh and groin. Whether a patient with molluscum contagiosum is treated or not is dependent on both the location and the symptoms the molluscum bodies are causing. Molluscum bodies located on the face, neck, and hands may need to be removed to prevent the virus from spreading to others.