Side Effects Of Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a minimally invasive procedure and induces the renewal of the texture and tone of an individual's skin. Numerous skin-related conditions and concerns can be addressed by microdermabrasion, including wrinkles, age spots, melasma, sun damage, fine lines, acne scarring, and several other conditions. A specialized applicator equipped with an abrasive surface is used to erode the tough outer layer of an individual's skin to rejuvenate it. A different technique of microdermabrasion can be utilized where fine particles of sodium bicarbonate or aluminum oxide are sprayed on the individual's skin to erode the dead skin cells that make up the tough outer layer.
Microdermabrasion is a safe and tolerable procedure for the skin colors and types of most individuals, but side effects can occur.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation

An individual who has microdermabrasion may experience a side effect referred to as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is a term used to describe patches of discolored skin that are flat and develop following damage to the epidermis or dermis. Microdermabrasion can cause melanin inside of the skin cells or keratinocytes to become displaced because of the post-damage inflammation. When this displacement of melanin occurs in the skin cells, melanin synthesis is increased in the melanocytes to replace what has been eroded. Displaced melanin in the skin cells can also become trapped by cells referred to as macrophages when it occurs in the lower layers of the epidermis. Individuals who have tan or darker skin tend to experience an alteration in the color of their skin following a microdermabrasion procedure more often than those with lighter colored skin. The new skin layer revealed by the mechanism of microdermabrasion may have less or more pigmentation than the layer that has been exfoliated.
Uncover additional side effects linked to microdermabrasion now.
Skin Tightness

Skin tightness is not an uncommon adverse side effect reported by individuals who have had microdermabrasion. The elastic ability of the skin to stretch is greatly determined by the amount of moisture that is present. Moisture allows the cells of the skin to be lubricated next to one another, rather than sticking together. Microdermabrasion strips the natural layer of oil that keeps moisture in the skin, which causes it to become unusually dry following the procedure. Because the epidermis is dry, the keratinocytes tend to have a harder time stretching and maintaining their elasticity. The membranes of the affected individual's skin cells adhere to each other, which causes the skin to feel abnormally tight. In addition, the loss of moisture causes the cells of the skin to shrink. When the skin cells shrink and stick together, the surface of the skin and its elasticity will decrease. Some individuals experience tightness of the skin because of the swelling that occurs after microdermabrasion due to inflammation.
Read more about microdermabrasion side effects now.
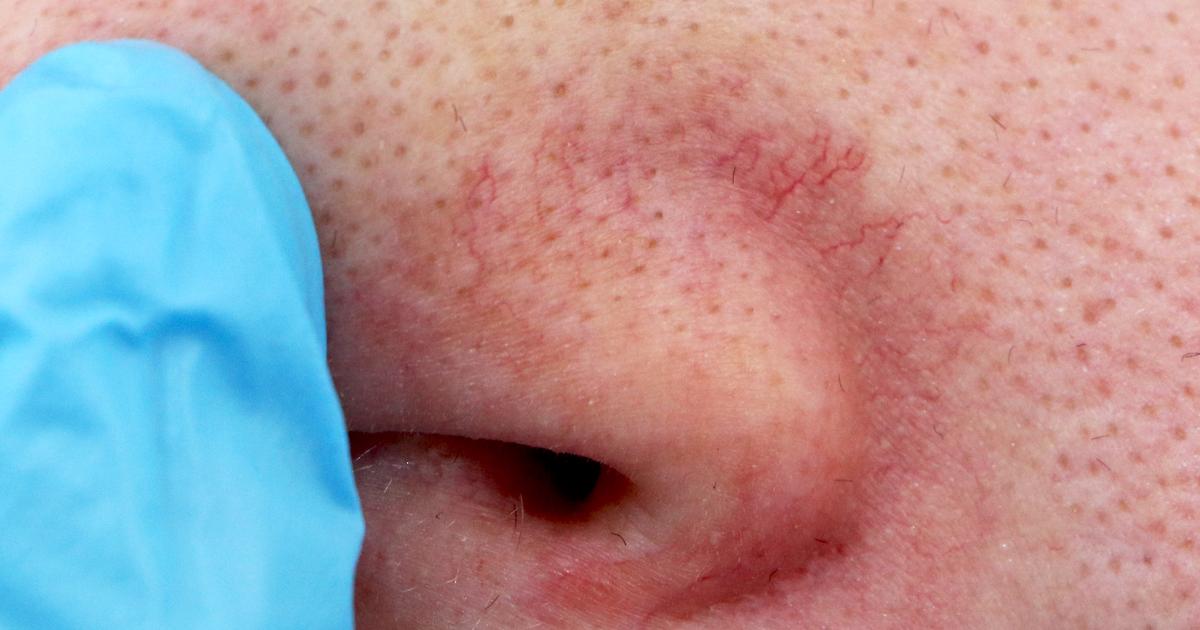
Swelling And Tenderness
An individual who undergoes microdermabrasion will most likely experience swelling and tenderness in the treated area. Microdermabrasion uses a diamond tip or small solid crystals sprayed onto the outer layer of the skin. This mechanism is similar to what happens when an individual rubs sandpaper on a wood surface. This type of skin buffing directly causes irritation and redness because the immune system reacts to minor damage to the outer layer of the skin. The individual's immune system responds by sending a myriad of different cells and substances to the site of the cellular damage. To get these cells and immune system substances to the affected area, the blood vessels are forced to dilate. This dilation of an affected individual's blood vessels and the rush of white blood cells to the site of damage is what causes it to become swollen, tender, red, and warm to the touch.
Learn more about the possible side effects of microdermabrasion now.
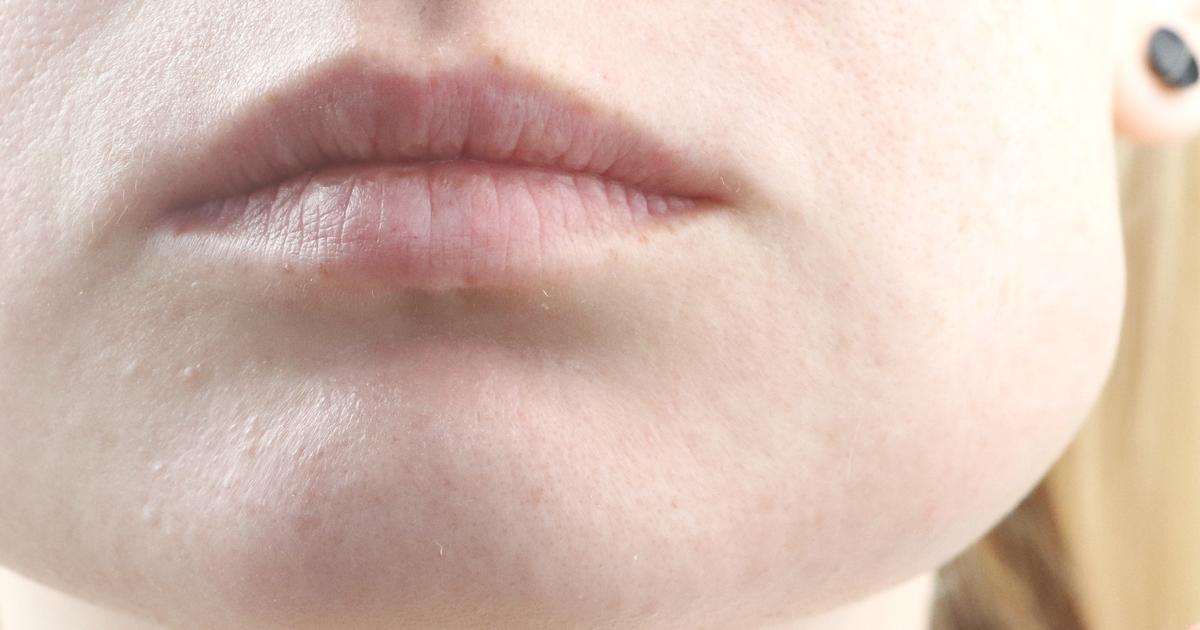
Minor Bruising
An individual who undergoes microdermabrasion may experience minor bruising. Bruising occurs when blood vessels just underneath the skin become damaged or burst open and leak blood into the surrounding area. Thin-skinned areas like those around the lips and eyes are most likely to develop minor bruising following microdermabrasion. The damage that occurs to the blood vessels in the areas treated with this procedure is the result of a vacuum effect exerted by the microdermabrasion catheter. This vacuum on the catheter serves to suck away the debris and dead skin cells exfoliated from the individual's skin. An individual who does not have particularly thin or delicate skin and is treated by a skilled technician will usually not experience this side effect. Individuals who take certain medications such as blood thinners and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are at an increased risk of developing minor bruising due to microdermabrasion.
Keep reading to learn more about the potential side effects linked to microdermabrasion now.
Dry Skin

An individual who has had microdermabrasion may experience dry and flaky skin as a side effect of their procedure. The skin can retain its moisture because the dry and dead outer layer of skin cells can protect the layers underneath it from outside influences. Glands in the skin are also able to help retain this moisture by producing oils that protect the skin and seal it in. Microdermabrasion can cause the protective layer of oil on the skin to slough off with the dead skin cells being exfoliated. It takes between several days and a week for an individual's glands to heal from any injury and to begin producing oils normally. Some of the dried-out skin may flake off as it too becomes part of the dead layer of skin that is meant to be removed by microdermabrasion. While dry skin is a side effect of this procedure, it is also a reason why an individual may have it done. Stripping the skin of its protective oil can stimulate it to make more oil in the long term.