What Is Dermatology?
Dermatology is a medical specialty that focuses on the treatment and management of skin conditions. This branch of medicine also treats conditions of the hair and nails, and it includes both surgical and non-surgical treatments. Dermatologists perform physical examinations, prescribe medications, administer injections, and perform surgery. They can treat a variety of concerns, including skin cancer, dry skin, cysts, hair loss, and scars. Dermatologists have a minimum of twelve years of training, and some dermatologists may choose to specialize in the treatment of pediatric patients. Other dermatologists specialize in Mohs surgery, an operation designed to remove skin cancer, and dermatologists can also specialize in dermatopathology, a discipline that uses microscopic investigation to diagnose skin diseases.
An overview of dermatology is provided below.
Dermatologist Qualifications
Dermatologists are fully qualified medical doctors, and they complete at least twelve years of formal medical training. After attending college for four years, prospective dermatologists graduate with a bachelor's degree. Then, they attend four years of medical school to earn their medical degree (M.D.). This is followed by a year-long internship, and dermatologists also complete a residency program of at least three years. The residency program involves intensive specialization in dermatology, and residents complete at least twelve to sixteen thousand hours of training alongside experienced doctors. After completing the residency program, some dermatologists may choose to have another period of advanced training in specific dermatological issues; this is known as fellowship training. Dermatologists who have completed their residency can also choose to complete a board certification exam. The exam is given by the American Board of Dermatology, and it covers the knowledge and skills the dermatologist has learned during their years of study. If the candidate successfully passes the exam, they are considered a board-certified dermatologist. This designation is highly regarded in the field.
Uncover information on the conditions dermatology treats next.
What Conditions Dermatology Treats

Dermatologists treat more than three thousand different skin, hair, and nail conditions. They treat issues such as dry skin, acne, rashes, and eczema, and they also help in the treatment of warts, moles, birthmarks, and hemangiomas. Skin cancer is a major area of treatment for many dermatologists, and they are trained to identify precancerous and cancerous lesions that need removal. Additionally, dermatologists help patients with healing scars after surgery, and they assist individuals coping with itchy skin or allergies that affect the skin. In terms of hair, dermatologists are trained to evaluate and treat hair loss, and they are licensed to perform laser hair removal for unwanted hair. Dermatologists also treat other hair conditions such as dandruff. For nail complaints, these medical professionals help in the treatment of fungal infections and other changes to the nails. In addition to their medical work, dermatologists treat several cosmetic concerns. For example, they regularly perform laser removal of tattoos, and they treat fine lines and wrinkles as well.
Get familiar with the specific cosmetic procedures dermatologists perform next.
Cosmetic Procedures Dermatologists Perform
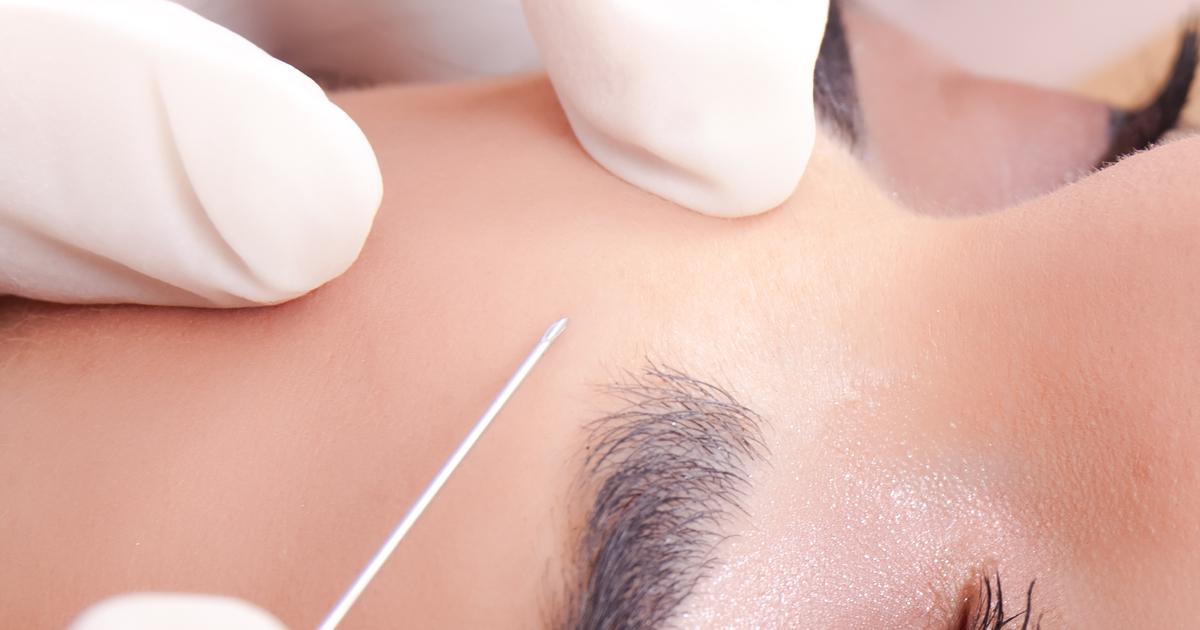
Dermatologists perform cosmetic procedures such as microdermabrasion and chemical peels to enhance the texture and tone of the skin, and they also treat fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots with topical treatments and injections of fillers or botulinum toxin A. They provide laser procedures for tattoo removal, and they can also treat scars, stretch marks, and saggy skin with laser skin resurfacing or laser skin tightening. Some dermatologists are trained in performing sclerotherapy to remove varicose veins, and these doctors treat acne with topical treatments and oral medications. Patients unhappy with the size or shape of their lips may choose to undergo a lip augmentation procedure with a cosmetic dermatologist, and this may involve fat injections and skin grafts. Dermatologists can perform neck liposuction procedures designed to reshape the neck, and patients might also choose to see a dermatologist for eyelid surgery. This operation takes one to three hours, and it is performed under general anesthesia. Unwanted skin and fat are removed from the eyelid area, and the eye muscles are tightened.
Discover details on the medical procedures dermatologists perform next.
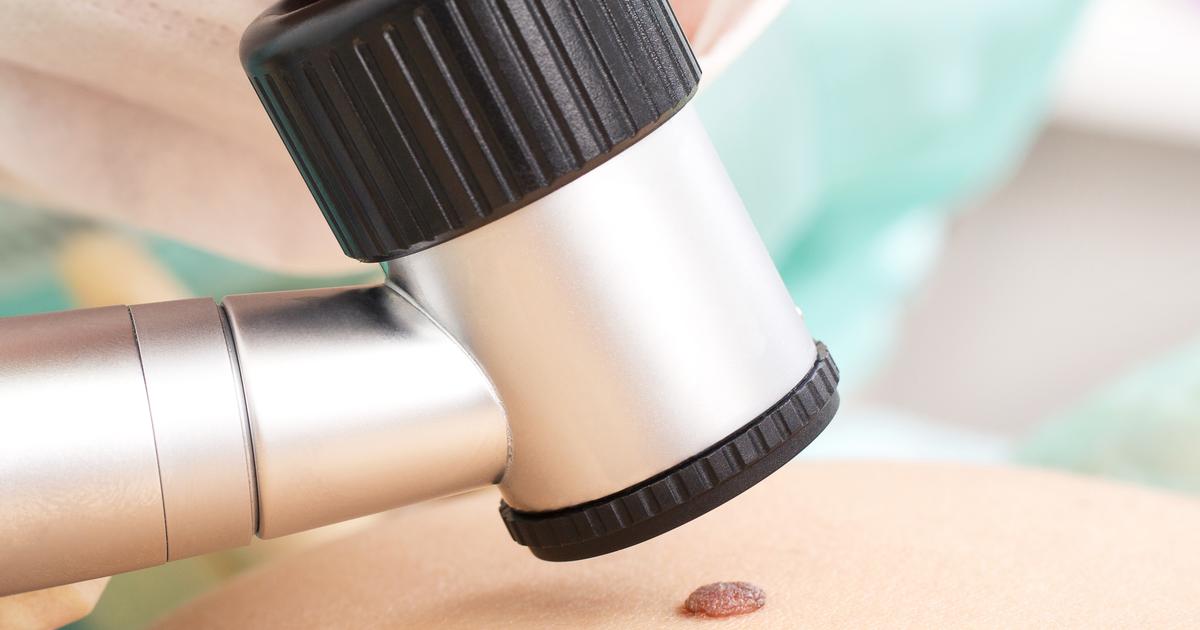
Medical Procedures Dermatologists Perform
Operations to remove precancerous and cancerous skin lesions are among the most common medical procedures dermatologists perform. After examining the lesion, the dermatologist may decide to perform a biopsy. This procedure uses a local anesthetic, and it involves removing a small area of the lesion. If cancer is detected, the dermatologist will remove the entire lesion and some of the surrounding skin. For advanced or large cancerous lesions, dermatologists may need to perform Mohs surgery. This procedure was developed in 1938, and it is performed under local anesthesia. The surgeon removes a small area of the lesion, and it is examined under a microscope. Depending on the results, the surgeon may continue removing deeper areas of the lesion until they reach a layer of skin where there are no cancerous cells. This procedure can take several hours, and recovery may take weeks or months. In addition to procedures for skin cancer, dermatologists perform cryotherapy for the removal of warts.
Learn about where dermatology works with other specialties next.
Where Dermatology Works With Other Specialties
Dermatologists routinely collaborate with doctors in other fields to manage a patient's care. They often collaborate with oncologists in the treatment of a patient's melanoma or other forms of skin cancer, and they may collaborate with ear, nose, and throat specialists for patients with issues in these areas. When treating patients with multiple medical issues, dermatologists may collaborate with cardiologists, internists, endocrinologists, and rheumatologists to get more information about the patient's health status or to follow up on their care. In a 2018 survey of dermatologists who treated female patients, roughly eighty percent of respondents reported collaborating with the patient's obstetrician or gynecologist, and over seventy percent reported they had collaborated with the patient's internist. Neurologists, nutritionists, and mental health professionals were among the other healthcare providers with whom the dermatologists collaborated. When performing surgery, dermatologists may ask for a plastic surgeon to be present to assist with particularly delicate or complex operations. Pediatric dermatologists typically collaborate with the child's pediatrician when planning and carrying out treatment.