What Causes Pain In The Knees?
Knee pain affects individuals of all ages, and it can be caused by injuries, infections, or disease. Patients might experience pain in the knee joint itself, and pain could also occur in the soft tissues surrounding the joint. Symptoms associated with knee pain include swelling or warmth around the area, stiffness, and joint instability. Patients might notice popping or crunching sounds coming from the knee as they move, and localized redness may develop. Depending on the severity of the pain, affected individuals might be unable to bend or straighten their knee, and it may be impossible to bear weight on the knee.
Doctors assess knee pain by performing a physical examination. They start by gently touching the area to check for tenderness, bruising, swelling, and structural changes. They will also push and pull on the knee, and the patient will be asked to raise and lower the leg in various directions. X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasounds may be useful in determining the underlying cause of knee pain and developing an appropriate treatment plan. Physical therapy could be appropriate, and doctors might suggest the use of injectable corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, or platelet-rich plasma. Surgery, including partial and complete knee replacement, could be considered for patients with specific knee injuries or severe knee pain.
The conditions described below are some of the major causes of knee pain.
Dislocated Kneecap

Patients could develop a dislocated kneecap as a result of a sudden change in direction while the leg is firmly planted. This frequently happens in contact sports such as basketball, and it could also occur after falls or other trauma. In the majority of kneecap dislocations, the patella (a triangular bone that protects the knee) slips toward the outer side of the leg. Patients may notice an obvious knee deformity, and they will usually be unable to walk or straighten the knee. The joint could swell too. To diagnose a dislocated kneecap, doctors will perform x-rays or MRI scans of the knee. Patients who have a confirmed dislocation will need to have their kneecap manipulated back to its proper location, and the knee will be placed in a cast or an immobilizer for roughly three weeks. After that time, physical therapy will be needed to rebuild strength and function in the joint. Kneecap dislocations typically heal within six weeks.
Uncover another cause of pain in the knees now.
ACL Injury
An ACL injury involves a partial or complete tear of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee. Patients who play contact sports such as soccer, football, and basketball are at an especially high risk of this type of injury. Running diagonally down the center of the knee, the anterior cruciate ligament is responsible for the rotational stability of the joint, and it also ensures the tibia stays in place. Doctors use the term 'sprain' to describe an injured ligament, and ACL sprains are divided into three categories according to severity. Most ACL injuries are complete or nearly complete sprains; these are much more common than partial tears of the ligament. Patients who have had an ACL injury might hear a popping noise at the time of the injury, and they could feel their knee give out from under them. There might also be discomfort while walking, and the knee generally swells within twenty-four hours of the injury. ACL injuries are typically treated with surgery using a tissue graft to reconstruct the ligament.
Read more about what causes knee pain now.
Torn Meniscus
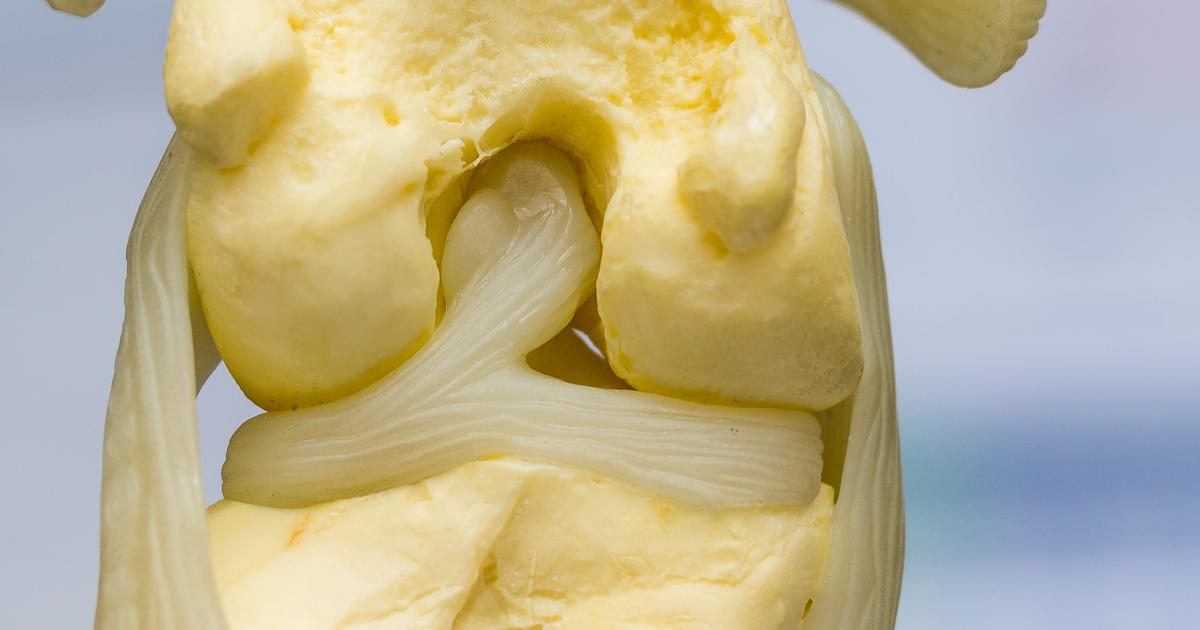

The meniscus is a thin piece of cartilage that provides cushioning between the bones of the shin and thigh. Each knee has two menisci, and these may tear as a result of the forceful rotation of the knee. Kneeling, squatting, or making sudden stops or turns could cause a torn meniscus. Patients with this injury might observe swelling and stiffness in the knee, and it could be difficult to fully straighten the joint. The knee may feel locked into place. To evaluate this injury, doctors perform a physical examination that includes watching the patient walk and squat. MRI scans will be needed, and an arthroscopy could be recommended in some cases. If a torn meniscus is confirmed, doctors usually start treatment with rest, ice, physical therapy, and pain relievers. Patients who continue to have severe pain or a locked knee after these conservative treatments will be considered for surgery. Children and young adults may be able to have a torn meniscus surgically repaired. If this is not an option for the patient, the surgeon will trim the meniscus instead.
Learn more about what can cause pain in the knees now.
Tendinitis
Tendinitis of the knee is normally caused as a result of a knee injury or inflammation in the area. The patellar tendon, a band of tissue that connects the patella and tibia, is an especially common site for tendinitis. Patients with this condition may have pain at the base of the kneecap, and this could progress to a burning sensation. Pain might increase while kneeling or squatting, and mild swelling may develop. When tendinitis first begins, patients will typically notice intermittent pain after exercise. As the condition advances, pain becomes more constant, and it could disrupt sleep and sports performance. Daily activities such as using stairs or riding in a car could become very painful. Tendinitis is generally treated with physical therapy, rest, ice, anti-inflammatories, and activity modification. Some patients may recover in a few weeks, and others could experience symptoms for several months.
Get more details on the various causes of knee pain now.
Sprained Ligaments

Ligaments connect two bones together, and sprained ligaments may develop after an injury or accident. The knee is supported by four main ligaments: the anterior cruciate ligament, posterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and lateral collateral ligament. In addition to these ligaments, many smaller ligaments are also routinely injured. Individuals who have sprained ligaments could experience swelling, pain, stiffness, and instability or buckling of the knee. Sports injuries, falls, and car accidents are common causes of this type of injury. If imaging studies confirm the presence of one or more sprained ligaments, treatment will be tailored to the specific ligament that is injured. Some types of ligament sprains may respond well to bracing, physical therapy, and other conservative treatments, and more serious sprains may need surgery.