Causes Of Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis refers to a condition that causes the optic nerve of the eye to swell. This nerve is crucial for vision, carrying light signals from the rear of the eye through to the brain. If this nerve swells or becomes damaged, vision will be negatively impacted, causing blurriness. Although physicians are not exactly sure what the precise cause of optic neuritis is, several conditions are known to lead to it. Typically, these are conditions that cause the immune system to mistakenly attack the tissue in the optic nerve, erroneously perceiving it as infected by a foreign invader. Such conditions are discussed in the following article.
Multiple Sclerosis

Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a debilitating disease that attacks the body's central nervous system. It disrupts the neural connections and flow of information between the brain and other parts of the body in an unpredictable and often aggressive way, inhibiting a person's ability to control those areas. The precise causes of multiple sclerosis are unknown, though researchers and physicians believe it develops after an individual who is already genetically predisposed encounters an environmental factor. Multiple sclerosis is known to cause inflammation and damage in the brain and spinal cord, including to the optic nerve. In fact, optic neuritis is often one of the first symptoms of multiple sclerosis in patients.
Learn about the next condition known to lead to optic neuritis now.
Schilder's Disease

Schilder's disease is thought to be a variant of multiple sclerosis, as it resembles the disease in both symptoms and pathology. Schilder's disease affects the brain and causes impairments with movement, speech, memory, and vision. It is a sporadic but progressive, degenerative disorder that attacks the central nervous system. The disease usually begins during childhood but can present in early adulthood as well. It is a demyelinating disease, which means the protective myelin sheath surrounding and protecting neurons becomes progressively damaged. Eventually, it is destroyed altogether. This damage significantly impairs the nerves' ability to conduct signals, such as those necessary for vision.
Continue reading to discover another condition that can result in optic neuritis now.
Mumps And Measles
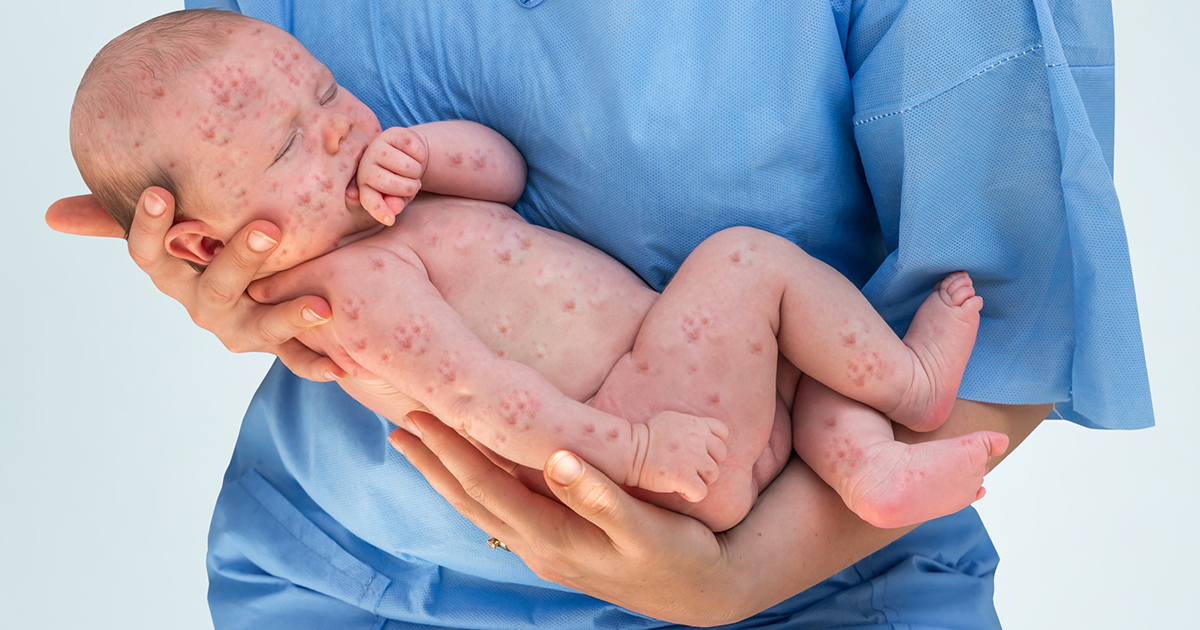
Viral infections, most notably mumps and measles, have also been shown to cause inflammation and sometimes permanent damage in the body. Measles is a highly contagious, infectious virus that usually only presents in developing countries. However, it has reemerged in developed countries in recent years as fewer individuals utilize the vaccine. In addition to its presentation on the skin, it also causes a runny nose, cough, and inflammation in the eyes.
Mumps is another infectious viral infection that leads to optic neuritis. This virus causes swelling, typically in the glands around the throat. Though it is most common in children, it can also affect adults. Vision problems are not as prevalent in mumps cases, but if the infection spreads, the optic nerve can become impaired.
Get the details on more conditions that can cause optic neuritis now.
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Guillain-Barre syndrome is also linked to optic neuritis. This rare neurological disorder is also characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissues, this time in the peripheral nervous system, which is made up of nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. Guillain-Barre syndrome comes in varying degrees, from mild to severe, even causing paralysis. It can affect anyone at any age, and researchers are still unsure of its precise causes. Weakness in the appendages of the body begin to present and, within two weeks, a patient can experience problems with swallowing and vision due to the attack on the optic nerve.
Learn more about what medical conditions can cause optic neuritis now.
Sarcoidosis

Sarcoidosis is another disease that causes inflammation in the body, most notably in the lungs and the lymph glands. It often causes nodules to grow in the inflamed tissue, which in turn alter the normal structure and functioning of the affected organs. The eyes can be affected by this disease, with the optic nerve being the number one affected nerve in patients, though symptoms outside of the thoracic area make up a much smaller percentage of reported symptoms by individuals affected. Patients tend to experience swelling and redness in the eyes as a symptom of the disease, though it is said damage to the optic nerve can often predate the diagnosis of sarcoidosis.